Adoptive immunotherapy with allodepleted donor T-cells improves immune reconstitution after haploidentical stem cell transplantation
- PMID: 16741253
- PMCID: PMC1895537
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-001909
Adoptive immunotherapy with allodepleted donor T-cells improves immune reconstitution after haploidentical stem cell transplantation
Abstract
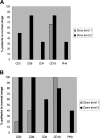
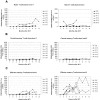
Poor T lymphocyte reconstitution limits the use of haploidentical stem cell transplantation (SCT) because it results in a high mortality from viral infections. One approach to overcome this problem is to infuse donor T cells from which alloreactive lymphocytes have been selectively depleted, but the immunologic benefit of this approach is unknown. We have used an anti-CD25 immunotoxin to deplete alloreactive lymphocytes and have compared immune reconstitution after allodepleted donor T cells were infused at 2 dose levels into recipients of T-cell-depleted haploidentical SCT. Eight patients were treated at 10(4) cells/kg/dose, and 8 patients received 10(5) cells/kg/dose. Patients receiving 10(5) cells/kg/dose showed significantly improved T-cell recovery at 3, 4, and 5 months after SCT compared with those receiving 10(4) cells/kg/dose (P < .05). Accelerated T-cell recovery occurred as a result of expansion of the effector memory (CD45RA(-)CCR-7(-)) population (P < .05), suggesting that protective T-cell responses are likely to be long lived. T-cell-receptor signal joint excision circles (TRECs) were not detected in reconstituting T cells in dose-level 2 patients, indicating they are likely to be derived from the infused allodepleted cells. Spectratyping of the T cells at 4 months demonstrated a polyclonal Vbeta repertoire. Using tetramer and enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assays, we have observed cytomegalovirus (CMV)- and Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-specific responses in 4 of 6 evaluable patients at dose level 2 as early as 2 to 4 months after transplantation, whereas such responses were not observed until 6 to 12 months in dose-level 1 patients. The incidence of significant acute (2 of 16) and chronic graft-versus-host disease (GVHD; 2 of 15) was low. These data demonstrate that allodepleted donor T cells can be safely used to improve T-cell recovery after haploidentical SCT and may broaden the applicability of this approach.
Figures
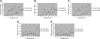



References
-
- Aversa F, Tabilio A, Velardi A, et al. Treatment of high-risk acute leukemia with T-cell-depleted stem cells from related donors with one fully mismatched HLA haplotype. N Engl J Med. 1998;339: 1186-1193. - PubMed
-
- Handgretinger R, Schumm M, Lang P, et al. Transplantation of megadoses of purified haploidentical stem cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999;872: 351-361. - PubMed
-
- Haddad E, Landais P, Friedrich W, et al. Long-term immune reconstitution and outcome after HLA-nonidentical T-cell-depleted bone marrow transplantation for severe combined immunodeficiency: a European retrospective study of 116 patients. Blood. 1998;91: 3646-3653. - PubMed
-
- Eyrich M, Lang P, Lal S, et al. A prospective analysis of the pattern of immune reconstitution in a paediatric cohort following transplantation of positively selected human leucocyte antigen-disparate haematopoietic stem cells from parental donors. Br J Haematol. 2001;114: 422-432. - PubMed
-
- Aversa F, Terenzi A, Tabilio A, et al. Full haplotype-mismatched hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation: a phase II study in patients with acute leukemia at high risk of relapse. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23: 3447-3454. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

