Mechanisms of sympathoadrenal failure and hypoglycemia in diabetes
- PMID: 16741570
- PMCID: PMC1464914
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI28735
Mechanisms of sympathoadrenal failure and hypoglycemia in diabetes
Abstract
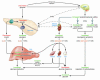
A reduced sympathoadrenal response, induced by recent antecedent hypoglycemia, is the key feature of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure (HAAF) and, thus, the pathogenesis of iatrogenic hypoglycemia in diabetes. Understanding of the mechanism(s) of that reduced response awaits new insight into its basic molecular, cellular, organ, and whole-body physiology and pathophysiology in experimental models. In this issue of the JCI, McCrimmon and colleagues report that application of urocortin I (a corticotrophin-releasing factor receptor-2 agonist) to the ventromedial hypothalamus reduces the glucose counterregulatory response to hypoglycemia in rats (see the related article beginning on page 1723). Thus, hypothalamic urocortin I release during antecedent hypoglycemia is, among other possibilities, a potential mechanism of HAAF.
Figures
Comment on
-
Corticotrophin-releasing factor receptors within the ventromedial hypothalamus regulate hypoglycemia-induced hormonal counterregulation.J Clin Invest. 2006 Jun;116(6):1723-30. doi: 10.1172/JCI27775. J Clin Invest. 2006. PMID: 16741581 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cryer P.E. Diverse causes of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure in diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004;350:2272–2279. - PubMed
-
- Cryer P.E. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure and its component syndromes in diabetes. Diabetes. 2005;54:3592–3601. - PubMed
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993;329:977–986. - PubMed

