The association between telomerase activity and expression of its RNA component (hTR) in breast cancer patients: the importance of DNase treatment
- PMID: 16749934
- PMCID: PMC1482692
- DOI: 10.1186/1477-3163-5-17
The association between telomerase activity and expression of its RNA component (hTR) in breast cancer patients: the importance of DNase treatment
Abstract
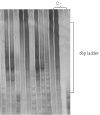
Telomerase is a ribonucleoprotein enzyme that compensates for the telomere length shortening which occurs during the cell cycle. Telomerase activity has been detected in most tumours but not in somatic cells. However, hTR; the RNA component of telomerase; has been reported to be universally expressed in both cancerous and non-cancerous tissues. Tumour samples from 50 patients with primary invasive breast cancer were collected. The TRAP assay was used to detect telomerase activity. RT-PCR on cDNA and DNased cDNA samples and control groups was used to detect the expression of hTR, GAPDH and PGM1 genes. Seventy-two percent of samples showed telomerase activity. DNA contamination was detected in 36 (72%) of RNA samples. Without performing DNase treatment, 49 (98%) of all samples showed hTR expression, but with the application of this strategy, hTR expression decreased from 98% to 64%. A significant association (p < 0.001) between hTR expression and telomerase activity was observed. Among the 32 hTR positive samples, 30 had telomerase activity and among the 18 hTR negative samples, telomerase activity was observed in 6 cases. Thus the application of this strategy could provide an applicable tool to use instead of the TRAP assay thus facilitating telomerase research in cancer genetic investigations.
Figures
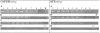
References
-
- Kim NW, Piatyszek MA, Prowse KR, Harley CB, West MD, Ho PL, Coviello GM, Wright WE, Weinrich SL, Shay JW. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994;266:2011–2015. - PubMed
-
- Liu BC-S, Larose I, Weinstein LJ, Ahn M, Weinstein MH, Richie JP. Expression of telomerse subunits in normal and neoplastic prostate epithelial cells isolated by laser capture microdisection. Am Cancer Soc. 2001;92:1943–1948. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

