A modified Hammersmith functional motor scale for use in multi-center research on spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 16750368
- PMCID: PMC3260054
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmd.2006.03.015
A modified Hammersmith functional motor scale for use in multi-center research on spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
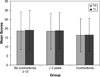
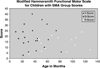
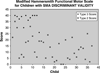
The Hammersmith functional motor scale for children with spinal muscular atrophy was modified to establish a standard measure of functional ability in children with non-ambulant spinal muscular atrophy types 2 and 3 in a longitudinal multi-center clinical trial. This study assessed the intra- and interrater reliability and the test-retest stability of a modified version of the scale. Both intra- and interrater reliability were established. Results indicate that the scale is reliable and stable over a 6 month period. Reliability was maintained when patient sample criteria were expanded to include children younger than 30 months and children with popliteal angles greater than 20 degrees . These data establish the modified Hammersmith functional motor scale for children with spinal muscular atrophy as a reliable instrument for use in multi-center treatment trials in non-ambulant spinal muscular atrophy children. Our data provides additional support for the use of original scale items in terms of ease of administration, usefulness and reliability, while incorporating modifications to optimize its use in a multi-center clinical research setting.
Figures

References
-
- Andreassi C, Angelozzi C, Tiziano FD, et al. Phenylbutyrate increases SMN expression in vitro: relevance for treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. Eur J Hum Genet. 2004;12(1):59–65. - PubMed
-
- Brahe C, Vitali T, Tiziano FD, et al. Phenylbutyrate increases SMN gene expression in spinal muscular atrophy patients. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005;13(2):256–259. - PubMed
-
- Crawford TO. Concerns about the design of clinical trials for spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2004;14(8–9):456–460. - PubMed
-
- Beenakker EA, van der Hoeven JH, Fock JM, Maurits NM. Reference values of maximum isometric muscle force obtained in 270 children aged 4–16 years by hand-held dynamometry. Neuromuscul Disord. 2001;11(5):441–446. - PubMed
-
- Merlini L, Solari A, Vita G, et al. Role of gabapentin in spinal muscular atrophy: results of a multicenter, randomized Italian study. J Child Neurol. 2003;18(8):537–541. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

