Accuracy and clinical utility of the CoaguChek XS portable international normalised ratio monitor in a pilot study of warfarin home-monitoring
- PMID: 16751303
- PMCID: PMC1860570
- DOI: 10.1136/jcp.2006.037820
Accuracy and clinical utility of the CoaguChek XS portable international normalised ratio monitor in a pilot study of warfarin home-monitoring
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the accuracy of the CoaguChek XS international normalised ratio (INR) monitor compared with the laboratory method.
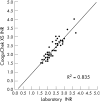
Methods: The accuracy and ease of use of the recently marketed CoaguChek XS portable INR monitor was evaluated in 17 patients involved in a trial of warfarin home monitoring. INR results from the monitor were compared with those from the laboratory method. Clinical applicability was measured by discrepant INR values, defined in the literature by expanded and narrow agreement criteria, and by the proportion of INR values differing by >15% and by >20% from those derived by the laboratory method.
Results: Participants provided 59 comparison INR measurements for analysis. The paired results were highly correlated (r = 0.91). Expanded and narrow agreement between paired INR values occurred 100% of the time. Only three CoaguChek XS (5.1%) results differed by >15% compared with the laboratory method; no results differed by >20% or were discrepant by >0.5 INR units.
Conclusions: In the hands of patients the CoaguChek XS showed good correlation with laboratory determination of INR and compared well with expanded and narrow clinical agreement criteria. Both patients and doctors were highly satisfied with the accuracy and ease of use of the CoaguChek XS.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical