The alkyl tert-butyl ether intermediate 2-hydroxyisobutyrate is degraded via a novel cobalamin-dependent mutase pathway
- PMID: 16751524
- PMCID: PMC1489616
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00080-06
The alkyl tert-butyl ether intermediate 2-hydroxyisobutyrate is degraded via a novel cobalamin-dependent mutase pathway
Abstract
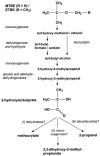
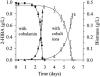
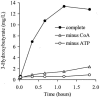
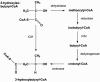
Fuel oxygenates such as methyl and ethyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE and ETBE, respectively) are degraded only by a limited number of bacterial strains. The aerobic pathway is generally thought to run via tert-butyl alcohol (TBA) and 2-hydroxyisobutyrate (2-HIBA), whereas further steps are unclear. We have now demonstrated for the newly isolated beta-proteobacterial strains L108 and L10, as well as for the closely related strain CIP I-2052, that 2-HIBA was degraded by a cobalamin-dependent enzymatic step. In these strains, growth on substrates containing the tert-butyl moiety, such as MTBE, TBA, and 2-HIBA, was strictly dependent on cobalt, which could be replaced by cobalamin. Tandem mass spectrometry identified a 2-HIBA-induced protein with high similarity to a peptide whose gene sequence was found in the finished genome of the MTBE-degrading strain Methylibium petroleiphilum PM1. Alignment analysis identified it as the small subunit of isobutyryl-coenzyme A (CoA) mutase (ICM; EC 5.4.99.13), which is a cobalamin-containing carbon skeleton-rearranging enzyme, originally described only in Streptomyces spp. Sequencing of the genes of both ICM subunits from strain L108 revealed nearly 100% identity with the corresponding peptide sequences from M. petroleiphilum PM1, suggesting a horizontal gene transfer event to have occurred between these strains. Enzyme activity was demonstrated in crude extracts of induced cells of strains L108 and L10, transforming 2-HIBA into 3-hydroxybutyrate in the presence of CoA and ATP. The physiological and evolutionary aspects of this novel pathway involved in MTBE and ETBE metabolism are discussed.
Figures

References
-
- Achten, C., A. Kolb, and W. Puttmann. 2002. Occurrence of methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) in riverbank filtered water and drinking water produced by riverbank filtration. 2. Environ. Sci. Technol. 36:3662-3670. - PubMed
-
- Andersen, M. D., P. K. Busk, I. Svendsen, and B. L. Møller. 2000. Cytochromes P-450 from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) catalyzing the first steps in the biosynthesis of the cyanogenic glucosides linamarin and lotaustralin. J. Biol. Chem. 275:1966-1975. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee, A., R. Sharma, and U. C. Banerjee. 2002. The nitrile-degrading enzymes: current status and future prospects. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 60:33-44. - PubMed
-
- Benndorf, D., I. Davidson, and W. Babel. 2004. Regulation of catabolic enzymes during long-term exposure of Delftia acidovorans MC1 to chlorophenoxy herbicides. Microbiology 150:1005-1014. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

