Development of Bacteroides 16S rRNA gene TaqMan-based real-time PCR assays for estimation of total, human, and bovine fecal pollution in water
- PMID: 16751534
- PMCID: PMC1489674
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01036-05
Development of Bacteroides 16S rRNA gene TaqMan-based real-time PCR assays for estimation of total, human, and bovine fecal pollution in water
Abstract
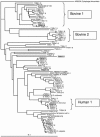
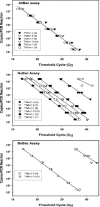
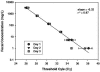
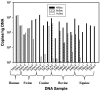
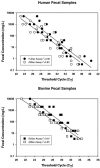
Bacteroides species are promising indicators for differentiating livestock and human fecal contamination in water because of their high concentration in feces and potential host specificity. In this study, a real-time PCR assay was designed to target Bacteroides species (AllBac) present in human, cattle, and equine feces. Direct PCR amplification (without DNA extraction) using the AllBac assay was tested on feces diluted in water. Fecal concentrations and threshold cycle were linearly correlated, indicating that the AllBac assay can be used to estimate the total amount of fecal contamination in water. Real-time PCR assays were also designed for bovine-associated (BoBac) and human-associated (HuBac) Bacteroides 16S rRNA genes. Assay specificities were tested using human, bovine, swine, canine, and equine fecal samples. The BoBac assay was specific for bovine fecal samples (100% true-positive identification; 0% false-positive identification). The HuBac assay had a 100% true-positive identification, but it also had a 32% false-positive rate with potential for cross-amplification with swine feces. The assays were tested using creek water samples from three different watersheds. Creek water did not inhibit PCR, and results from the AllBac assay were correlated with those from Escherichia coli concentrations (r2= 0.85). The percentage of feces attributable to bovine and human sources was determined for each sample by comparing the values obtained from the BoBac and HuBac assays with that from the AllBac assay. These results suggest that real-time PCR assays without DNA extraction can be used to quantify fecal concentrations and provide preliminary fecal source identification in watersheds.
Figures

References
-
- Altschul, S. F., W. Gish, W. Miller, E. W. Myers, and D. J. Lipman. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215:403-410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

