Three enzymes for trehalose synthesis in Bradyrhizobium cultured bacteria and in bacteroids from soybean nodules
- PMID: 16751539
- PMCID: PMC1489629
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00256-06
Three enzymes for trehalose synthesis in Bradyrhizobium cultured bacteria and in bacteroids from soybean nodules
Abstract
alpha,alpha-Trehalose is a disaccharide accumulated by many microorganisms, including rhizobia, and a common role for trehalose is protection of membrane and protein structure during periods of stress, such as desiccation. Cultured Bradyrhizobium japonicum and B. elkanii were found to have three enzymes for trehalose synthesis: trehalose synthase (TS), maltooligosyltrehalose synthase (MOTS), and trehalose-6-phosphate synthetase. The activity level of the latter enzyme was much higher than those of the other two in cultured bacteria, but the reverse was true in bacteroids from nodules. Although TS was the dominant enzyme in bacteroids, the source of maltose, the substrate for TS, is not clear; i.e., the maltose concentration in nodules was very low and no maltose was formed by bacteroid protein preparations from maltooligosaccharides. Because bacteroid protein preparations contained high trehalase activity, it was imperative to inhibit this enzyme in studies of TS and MOTS in bacteroids. Validamycin A, a commonly used trehalase inhibitor, was found to also inhibit TS and MOTS, and other trehalase inhibitors, such as trehazolin, must be used in studies of these enzymes in nodules. The results of a survey of five other species of rhizobia indicated that most species sampled had only one major mechanism for trehalose synthesis. The presence of three totally independent mechanisms for the synthesis of trehalose by Bradyrhizobium species suggests that this disaccharide is important in the function of this organism both in the free-living state and in symbiosis.
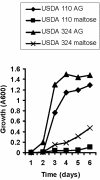
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional role of Bradyrhizobium japonicum trehalose biosynthesis and metabolism genes during physiological stress and nodulation.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010 Feb;76(4):1071-81. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02483-09. Epub 2009 Dec 18. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20023090 Free PMC article.
-
Enzymes of alpha,alpha-Trehalose Metabolism in Soybean Nodules.Plant Physiol. 1986 Jun;81(2):538-41. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.2.538. Plant Physiol. 1986. PMID: 16664852 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and physiological responses of Bradyrhizobium japonicum to desiccation-induced stress.J Bacteriol. 2007 Oct;189(19):6751-62. doi: 10.1128/JB.00533-07. Epub 2007 Jul 27. J Bacteriol. 2007. PMID: 17660288 Free PMC article.
-
New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule.Glycobiology. 2003 Apr;13(4):17R-27R. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwg047. Epub 2003 Jan 22. Glycobiology. 2003. PMID: 12626396 Review.
-
The role of Bradyrhizobium japonicum nitric oxide reductase in nitric oxide detoxification in soya bean root nodules.Biochem Soc Trans. 2006 Feb;34(Pt 1):195-6. doi: 10.1042/BST0340195. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006. PMID: 16417520 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Role of Trehalose in Tripartite Symbiosis Among Rhizobia, Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi, and Legumes for Enhancing Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants.Front Microbiol. 2020 Sep 17;11:509919. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.509919. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 33042042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolomic Profiling of Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens-Induced Root Nodules Reveals Both Host Plant-Specific and Developmental Signatures.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 27;17(6):815. doi: 10.3390/ijms17060815. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27240350 Free PMC article.
-
Importance of trehalose biosynthesis for Sinorhizobium meliloti Osmotolerance and nodulation of Alfalfa roots.J Bacteriol. 2009 Dec;191(24):7490-9. doi: 10.1128/JB.00725-09. Epub 2009 Oct 16. J Bacteriol. 2009. PMID: 19837796 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological and Molecular Aspects of Tolerance to Environmental Constraints in Grain and Forage Legumes.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Aug 13;16(8):18976-9008. doi: 10.3390/ijms160818976. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26287163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-poisoning of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by targeting GlgE in an alpha-glucan pathway.Nat Chem Biol. 2010 May;6(5):376-84. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.340. Epub 2010 Mar 21. Nat Chem Biol. 2010. PMID: 20305657 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ando, O., M. Nakajima, M. Kifune, H. Fang, and K. Tanzawa. 1995. Trehazolin, a slow, tight-binding inhibitor of silkworm trehalase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1244:295-302. - PubMed
-
- Cabib, E., and L. Leloir. 1958. The biosynthesis of trehalose-6-phosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 231:259-275. - PubMed
-
- De Smet, K. A., A. Weston, I. N. Brown, D. B. Young, and B. D. Robertson. 2000. Three pathways for trehalose biosynthesis in mycobacteria. Microbiology 146:199-208. - PubMed
-
- Elbein, A. D., Y. T. Pan, I. Pastuszak, and D. Carroll. 2003. New insights on trehalose: a multifunctional molecule. Glycobiology 13:17R-27R. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

