Internally controlled real-time PCR method for quantitative species-specific detection and vapA genotyping of Rhodococcus equi
- PMID: 16751540
- PMCID: PMC1489618
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02706-05
Internally controlled real-time PCR method for quantitative species-specific detection and vapA genotyping of Rhodococcus equi
Abstract
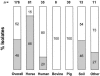
We developed a novel quantitative real-time PCR (Q-PCR) method for the soil actinomycete Rhodococcus equi, an important horse pathogen and emerging human pathogen. Species-specific quantification was achieved by targeting the chromosomal monocopy gene choE, universally conserved in R. equi. The choE Q-PCR included an internal amplification control (IAC) for identification of false negatives. A second Q-PCR targeted the virulence plasmid gene vapA, carried by most horse isolates but infrequently found in isolates from other sources. The choE-IAC and vapA assays were 100% sensitive and specific as determined using 178 R. equi isolates, 77 nontarget bacteria, and a panel of 60 R. equi isolates with known vapA+ and vapA-negative (including vapB+) plasmid genotypes. The vapA+ frequency among isolate types was as follows: horse, 85%; human, 20%; bovine and pig, 0%; others, 27%. The choE-IAC Q-PCR could detect up to one genome equivalent using R. equi DNA or 100 bacteria/ml using DNA extracted from artificially contaminated horse bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. Quantification was linear over a 6-log dynamic range down to approximately 10 target molecules (or 1,000 CFU/ml BAL fluid) with PCR efficiency E of >0.94. The vapA assay had similar performance but appeared unsuitable for accurate (vapA+) R. equi quantification due to variability in target gene or plasmid copy number (1 to 9). The dual-reaction Q-PCR system here reported offers a useful tool to both medical and veterinary diagnostic laboratories for the quantitative detection of R. equi and (optional) vapA+ "horse-pathogenic" genotype determination.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid determination of vapA/vapB genotype in Rhodococcus equi using a differential polymerase chain reaction method.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2004 May;85(4):317-26. doi: 10.1023/B:ANTO.0000020383.66622.4d. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2004. PMID: 15031644
-
Evaluation of a multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for simultaneous detection of Rhodococcus equi and the vapA gene.Am J Vet Res. 2005 Aug;66(8):1380-5. doi: 10.2460/ajvr.2005.66.1380. Am J Vet Res. 2005. PMID: 16173481
-
Molecular epidemiology of Rhodococcus equi based on traA, vapA, and vapB virulence plasmid markers.J Infect Dis. 2007 Sep 1;196(5):763-9. doi: 10.1086/519688. Epub 2007 Jul 13. J Infect Dis. 2007. PMID: 17674320
-
Molecular and infection biology of the horse pathogen Rhodococcus equi.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009 Sep;33(5):870-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2009.00181.x. Epub 2009 Apr 23. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2009. PMID: 19453748 Review.
-
Short review: Geographical distribution of equine-associated pVAPA plasmids in Rhodococcus equi in the world.Vet Microbiol. 2023 Dec;287:109919. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2023.109919. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Vet Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38000208 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Quantitative PCR for Rhodococcus equi and Macrolide Resistance Detection in Equine Respiratory Samples.Animals (Basel). 2022 May 3;12(9):1172. doi: 10.3390/ani12091172. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565598 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of Rhodococcus equi isolates in equines.Vet World. 2017 Jan;10(1):6-10. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2017.6-10. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Vet World. 2017. PMID: 28246441 Free PMC article.
-
VirS, an OmpR/PhoB subfamily response regulator, is required for activation of vapA gene expression in Rhodococcus equi.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Oct 3;14:243. doi: 10.1186/s12866-014-0243-1. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25281192 Free PMC article.
-
Development of quantitative real-time PCR assays for detection and quantification of surrogate biological warfare agents in building debris and leachate.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Oct;73(20):6557-65. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00779-07. Epub 2007 Aug 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17720820 Free PMC article.
-
Rhodococcus parequi sp. nov., a new species isolated from equine farm soil closely related to the pathogen Rhodococcus equi.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025 Mar;75(3):006679. doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.006679. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40063668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arriaga, J. M., N. D. Cohen, J. N. Derr, M. K. Chaffin, and R. J. Martens. 2002. Detection of Rhodococcus equi by polymerase chain reaction using species-specific nonproprietary primers. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 14:347-353. - PubMed
-
- Arya, B., S. Hussian, and S. Hariharan. 2004. Rhodococcus equi pneumonia in a renal transplant patient: a case report and review of literature. Clin. Transplant. 18:748-752. - PubMed
-
- Bell, K. S., J. C. Philp, N. Christofi, and D. W. Aw. 1996. Identification of Rhodococcus equi using the polymerase chain reaction. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 23:72-74. - PubMed
-
- Davis, W. P., B. A. Steficek, G. L. Watson, B. Yamini, H. Madarame, S. Takai, and J. A. Render. 1999. Disseminated Rhodococcus equi infection in two goats. Vet. Pathol. 36:336-339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

