Presynaptic opioid receptors on noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in the human as compared to the rat neocortex
- PMID: 16751796
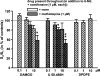
- PMCID: PMC1617080
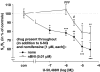
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706782
Presynaptic opioid receptors on noradrenergic and serotonergic neurons in the human as compared to the rat neocortex
Abstract
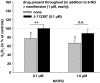
1. Electrically evoked release of [3H]-noradrenaline ([3H]-NA) or [3H]-5-hydroxytryptamine ([3H]-5-HT) in slices of human and the rat neocortex was used to characterize presynaptic opioid receptors. 2. Release of [3H]-NA in rat neocortical slices was reduced only by the mu-receptor agonist DAMGO (pIC50: 7.27, CI95: [7.22, 7.32]; Imax: 77.6+/-1.6%; antagonized by naloxone: pA2: 8.88, CI95: [8.78, 8.98]). 3. Release of [3H]-NA in human neocortical slices was unaffected by DAMGO, but inhibited by the delta-receptor agonist DPDPE (Imax: 25.7+/-2.2%) and the kappa-receptor agonist U-50,488H (19.7+/-2.7% inhibition at 1 microM). Both effects were antagonized by naltrindole (1 microM). 4. Release of [3H]-5-HT in rat neocortical slices, was inhibited by DAMGO (10 microM) and U-50,488H (1 and 10 microM) only in the presence of the 5-HT receptor antagonist methiotepin (1 microM). 5. Release of [3H]-5-HT in human neocortical slices was unaffected by DPDPE, but U-50,488H (Imax: 40.8+/-8.3%; antagonized by 0.1 microM norbinaltorphimine) and DAMGO (16.4+/-3.9% inhibition at 1 microM; antagonized by 0.1 microM naloxone) acted inhibitory. 6. Release of [3H]-5-HT in human neocortical slices was reduced by nociceptin/orphanin (0.1 and 1 microM). These effects were antagonized by the ORL1 antagonist J-113397 (1-[(3R,4R)-1-cyclo-octylmethyl-3-hydroxymethyl-4-piperidyl]-3-ethyl-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one; 0.1 microM). 7. This study provides evidence for significant species differences in opioid receptor-mediated modulation of NA and 5-HT-release in human vs rat neocortex. In rats, mu-opioid receptors modulate NA release, but 5-HT release is only weakly affected by mu- and kappa-opioids. In contrast, NA release in human neocortex is modulated via delta-opioid receptors, but 5-HT release mainly via kappa-opioid receptors. In addition also the ORL1 receptor seems to be involved in 5-HT release modulation.
Figures




References
-
- ALTMAN D.G. Statistics in medical journals: developments in the 1980s. Stat. Med. 1991;10:1897–1913. - PubMed
-
- BIRCH P.J., HAYES A.G., SHEEHAN M.J., TYERS M.B. Norbinaltorphimine: antagonist profile at kappa opioid receptors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1987;144:405–408. - PubMed
-
- BLACKBURN T.P., CROSS A.J., HILLE C., SLATER P. Autoradiographic localization of delta opiate receptors in rat and human brain. Neuroscience. 1988;27:497–506. - PubMed
-
- CLARK J.A., ITZHAK Y., HRUBY V.J., YAMAMURA H.I., PASTERNAK G.W. [D-Pen2,D-Pen5]enkephalin (DPDPE): a delta-selective enkephalin with low affinity for mu 1 opiate binding sites. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1986;128:303–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

