Nepmucin, a novel HEV sialomucin, mediates L-selectin-dependent lymphocyte rolling and promotes lymphocyte adhesion under flow
- PMID: 16754720
- PMCID: PMC2118321
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20052543
Nepmucin, a novel HEV sialomucin, mediates L-selectin-dependent lymphocyte rolling and promotes lymphocyte adhesion under flow
Abstract
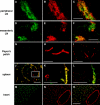
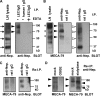
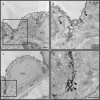
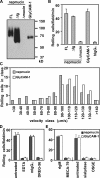
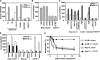
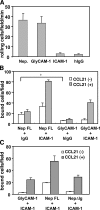
Lymphocyte trafficking to lymph nodes (LNs) is initiated by the interaction between lymphocyte L-selectin and certain sialomucins, collectively termed peripheral node addressin (PNAd), carrying specific carbohydrates expressed by LN high endothelial venules (HEVs). Here, we identified a novel HEV-associated sialomucin, nepmucin (mucin not expressed in Peyer's patches [PPs]), that is expressed in LN HEVs but not detectable in PP HEVs at the protein level. Unlike conventional sialomucins, nepmucin contains a single V-type immunoglobulin (Ig) domain and a mucin-like domain. Using materials affinity-purified from LN lysates with soluble L-selectin, we found that two higher molecular weight species of nepmucin (75 and 95 kD) were decorated with oligosaccharides that bind L-selectin as well as an HEV-specific MECA-79 monoclonal antibody. Electron microscopic analysis showed that nepmucin accumulates in the extended luminal microvillus processes of LN HEVs. Upon appropriate glycosylation, nepmucin supported lymphocyte rolling via its mucin-like domain under physiological flow conditions. Furthermore, unlike most other sialomucins, nepmucin bound lymphocytes via its Ig domain, apparently independently of lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 and very late antigen 4, and promoted shear-resistant lymphocyte binding in combination with intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Collectively, these results suggest that nepmucin may serve as a dual-functioning PNAd in LN HEVs, mediating both lymphocyte rolling and binding via different functional domains.
Figures


References
-
- von Andrian, U.H., and T.R. Mempel. 2003. Homing and cellular traffic in lymph nodes. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3:867–878. - PubMed
-
- Miyasaka, M., and T. Tanaka. 2004. Lymphocyte trafficking across high endothelial venules: dogmas and enigmas. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 4:360–370. - PubMed
-
- Rosen, S.D. 2004. Ligands for L-selectin: homing, inflammation, and beyond. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 22:129–156. - PubMed
-
- Yeh, J.C., N. Hiraoka, B. Petryniak, J. Nakayama, L.G. Ellies, D. Rabuka, O. Hindsgaul, J.D. Marth, J.B. Lowe, and M. Fukuda. 2001. Novel sulfated lymphocyte homing receptors and their control by a Core1 extension β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase. Cell. 105:957–969. - PubMed
-
- Maly, P., A. Thall, B. Petryniak, C.E. Rogers, P.L. Smith, R.M. Marks, R.J. Kelly, K.M. Gersten, G. Cheng, T.L. Saunders, et al. 1996. The α(1,3)fucosyltransferase Fuc-TVII controls leukocyte trafficking through an essential role in L-, E-, and P-selectin ligand biosynthesis. Cell. 86:643–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

