Effectiveness of cigarette warning labels in informing smokers about the risks of smoking: findings from the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Four Country Survey
- PMID: 16754942
- PMCID: PMC2593056
- DOI: 10.1136/tc.2005.012294
Effectiveness of cigarette warning labels in informing smokers about the risks of smoking: findings from the International Tobacco Control (ITC) Four Country Survey
Abstract
Background: Health warnings on cigarette packages are among the most common means of communicating the health risks of smoking. However, few studies have evaluated the impact of package warnings on consumer knowledge about tobacco risks.
Objective: The aim of the current study was to use nationally representative samples of adult smokers from the United States (USA), the United Kingdom (UK), Canada (CAN), and Australia (AUS) from the International Tobacco Control Four Country Survey (ITC-4) to examine variations in smokers' knowledge about tobacco risks and the impact of package warnings.
Methods: A telephone survey was conducted with 9058 adult smokers from the following countries: USA (n = 2138), UK (n = 2401), CAN (n = 2214) and AUS (n = 2305). Respondents were asked to state whether they believed smoking caused heart disease, stroke, impotence, lung cancer in smokers, and lung cancer in non-smokers. Respondents were also asked whether the following chemicals are found in cigarette smoke: cyanide, arsenic and carbon monoxide.
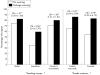
Findings: Smokers in the four countries exhibited significant gaps in their knowledge of the risks of smoking. Smokers who noticed the warnings were significantly more likely to endorse health risks, including lung cancer and heart disease. In each instance where labelling policies differed between countries, smokers living in countries with government mandated warnings reported greater health knowledge. For example, in Canada, where package warnings include information about the risks of impotence, smokers were 2.68 (2.41-2.97) times more likely to agree that smoking causes impotence compared to smokers from the other three countries.
Conclusion: Smokers are not fully informed about the risks of smoking. Warnings that are graphic, larger, and more comprehensive in content are more effective in communicating the health risks of smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: none declared
References
-
- Murray C J, Lopez A D. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet 19973491498–1504. - PubMed
-
- US Department of Health and Human Services The health consequences of smoking: a report of the Surgeon General. p. 2004.
-
- Janz N, Becker M H. The health belief model: a decade later. Health Educ Q 1984111–47. - PubMed
-
- Bandura A. Self‐efficacy: toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychol Rev 197784191–215. - PubMed
-
- Ajzen I. The theory of planned behavior. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 199150179–211.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical