Energy transduction: proton transfer through the respiratory complexes
- PMID: 16756489
- PMCID: PMC2659341
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.75.062003.101730
Energy transduction: proton transfer through the respiratory complexes
Abstract
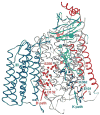
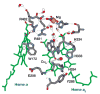
A series of metalloprotein complexes embedded in a mitochondrial or bacterial membrane utilize electron transfer reactions to pump protons across the membrane and create an electrochemical potential (DeltamuH+). Current understanding of the principles of electron-driven proton transfer is discussed, mainly with respect to the wealth of knowledge available from studies of cytochrome c oxidase. Structural, experimental, and theoretical evidence supports the model of long-distance proton transfer via hydrogen-bonded water chains in proteins as well as the basic concept that proton uptake and release in a redox-driven pump are driven by charge changes at the membrane-embedded centers. Key elements in the pumping mechanism may include bound water, carboxylates, and the heme propionates, arginines, and associated water above the hemes. There is evidence for an important role of subunit III and proton backflow, but the number and nature of gating mechanisms remain elusive, as does the mechanism of physiological control of efficiency.
Figures
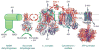
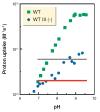
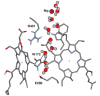
References
-
- Mills DA, Schmidt B, Hiser C, Westley E, Ferguson-Miller S. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:14894–901. - PubMed
-
- Kadenbach B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2003;1604:77–94. - PubMed
-
- Brand MD, Buckingham JA, Esteves TC, Green K, Lambert AJ, et al. Biochem Soc Symp. 2004;71:203–13. - PubMed
-
- Lanyi JK. Annu Rev Physiol. 2004;66:665–88. - PubMed
-
- Hunte C, Palsdottir H, Trumpower BL. FEBS Lett. 2003;545:39–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

