Ser18 and 23 phosphorylation is required for p53-dependent apoptosis and tumor suppression
- PMID: 16757976
- PMCID: PMC1478190
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601167
Ser18 and 23 phosphorylation is required for p53-dependent apoptosis and tumor suppression
Abstract
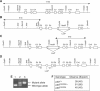
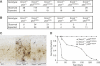
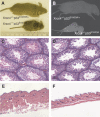
Mouse p53 is phosphorylated at Ser18 and Ser23 after DNA damage. To determine whether these two phosphorylation events have synergistic functions in activating p53 responses, we simultaneously introduced Ser18/23 to Ala mutations into the endogenous p53 locus in mice. While partial defects in apoptosis are observed in p53S18A and p53S23A thymocytes exposed to IR, p53-dependent apoptosis is essentially abolished in p53S18/23A thymocytes, indicating that these two events have critical and synergistic roles in activating p53-dependent apoptosis. In addition, p53S18/23A, but not p53S18A, could completely rescue embryonic lethality of Xrcc4(-/-) mice that is caused by massive p53-dependent neuronal apoptosis. However, certain p53-dependent functions, including G1/S checkpoint and cellular senescence, are partially retained in p53(S18/23A) cells. While p53(S18A) mice are not cancer prone, p53S18/23A mice developed a spectrum of malignancies distinct from p53S23A and p53(-/-) mice. Interestingly, Xrcc4(-/-)p53S18/23A mice fail to develop tumors like the pro-B cell lymphomas uniformly developed in Xrcc4(-/-) p53(-/-) animals, but exhibit developmental defects typical of accelerated ageing. Therefore, Ser18 and Ser23 phosphorylation is important for p53-dependent suppression of tumorigenesis in certain physiological context.
Figures
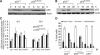



References
-
- Bischoff F, Yim S, Pathak S, Grant G, Siciliano M, Giovanella B, Strong L, Tainsky M (1990) Spontaneous abnormalities in normal fibroblasts from patients with Li-Fraumeni cancer syndrome: aneuploidy and immortalization. Cancer Res 50: 7979–7984 - PubMed
-
- Blaschke JAW, Chun J (1998) Programmed cell death is a universal feature of embryonic and postnatal neuroproliferative regions throughout the central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 396: 39–50 - PubMed
-
- Blaschke A, Staley K, Chun J (1996) Widespread programmed cell death in proliferative and postmitotic regions of the fetal cerebral cortex. Development 122: 1165–1174 - PubMed
-
- Borges HL, Chao C, Xu Y, Linden R, Wang JY (2004) Radiation-induced apoptosis in developing mouse retina exhibits dose-dependent requirement for ATM phosphorylation of p53. Cell Death Differ 11: 494–502 - PubMed
-
- Bouffler S, Kemp C, Balmain A, Cox R (1995) Spontaneous and ionizing radiation-induced chromosomal abnormalities in p53-deficient mice. Cancer Res 55: 3883–3889 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

