Mapping of rat hippocampal neurons with NeuN after ischemia/reperfusion and Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) pretreatment
- PMID: 16758319
- PMCID: PMC11520701
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-006-9080-6
Mapping of rat hippocampal neurons with NeuN after ischemia/reperfusion and Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) pretreatment
Abstract
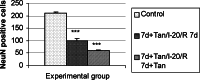
1. The neuroprotective effect of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) against transient forebrain ischemia following 7 days of reperfusion was studied in male Wistar rats after four-vessel occlusion for 20 min. 2. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein was used for immunohistochemical detection of surviving pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus, as well as counterstaining with hematoxylin in the same sections for detection of neurons that underwent delayed neuronal death and for glial nuclei staining. GFAP immunohistochemistry was used for detection of astrocytes in the studied area of CA1 region. 3. In the group of rats pretreated 7 days with Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761), following 20 min of ischemia and 7 days of reperfusion without EGb 761, increased number of NeuN immunoreactive cells were counted in the most vulnerable CA1 pyramidal layer of hippocampus. On the other hand, the group of rats with 7 days of EGb 761 pretreatment following 20 min of ischemia and 7 days of reperfusion with EGb 761 showed decreased number of surviving NeuN immunoreactive CA1 pyramidal cells in comparison with the first above-mentioned experimental group. 4. Increased number of reactive astrocytes immunolabeled for GFAP (Glial fibrilary acidic protein) was observed in both experimental groups in the stratum oriens and stratum lacunosum and moleculare. 5. Twenty minutes of ischemia is lethal for most population of CA1 pyramidal cell layer. Our results showed that prophylactic oral administration of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) in the dose 40 mg/kg/day during the 7 days protects the most vulnerable CA1 pyramidal cells against 20 min of ischemia.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Effect of antioxidant treatment in global ischemia and ischemic postconditioning in the rat hippocampus.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Sep;29(6-7):837-44. doi: 10.1007/s10571-009-9365-7. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19259806 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide, a component of the Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761), in gerbil global brain ischemia.Brain Res. 2001 Dec 20;922(2):282-92. doi: 10.1016/s0006-8993(01)03188-2. Brain Res. 2001. PMID: 11743961
-
[Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against excitotoxicity induced by NMDA receptors and mechanism thereof].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006 Sep 19;86(35):2479-84. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17156678 Chinese.
-
Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of Ginkgo biloba extract for Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003 Jun;36 Suppl 1:S8-14. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40454. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 13130383 Review.
-
[Protective effects of a Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) on ischemia-reperfusion injury].Therapie. 2001 Sep-Oct;56(5):595-600. Therapie. 2001. PMID: 11806299 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Compounds and Traditional Herbal Medicine: Promising Approaches for the Treatment of Dementia.Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2021 Apr 12;11:1-14. doi: 10.2147/DNND.S299589. eCollection 2021. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis. 2021. PMID: 33880073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular Contributions to Cognitive Impairment and Treatments with Traditional Chinese Medicine.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:9627258. doi: 10.1155/2016/9627258. Epub 2016 Nov 23. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 28042305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnopharmacological Approaches for Dementia Therapy and Significance of Natural Products and Herbal Drugs.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Feb 12;10:3. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00003. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29483867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on the structure of Cornu Ammonis in aged rat: A morphometric study.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015 Sep;18(9):932-7. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26523225 Free PMC article.
-
Less hippocampal neuronal death in young gerbils following transient global cerebral ischemia is associated with long‑term maintenance of insulin‑like growth factor 1 and its receptors in the hippocampal CA1 region.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Feb;17(2):3055-3061. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.8243. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29257289 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bodsch, W., Takahashi, K., Barbier, A., Ophoff, B. G., and Hossmann, K. A. (1985). Cerebral protein synthesis and ischemia. Prog. Brain Res.63:197–210. - PubMed
-
- Calapai, G., Crupi, A., Firenzuoli, F., Marciano, M. C., Squadrito, F., Inferrera, G., Parisi, G., Rizzo, A., Crisafulli, C., Fiore, A., and Caputi, A. P. (2000). Neuroprotective effect of Ginkgo biloba extract in brain ischemia are mediated by inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis. Life Sci.67:2673–2683. - PubMed
-
- Chandrasekaran, K., Mehrabian, Z., Spinnewyn, B., Drieu, K., and Fiskum, G. (2001). Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide, a component of the Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761), in gerbil global brain ischemia. Brain Res.922:282–292. - PubMed
-
- Chen, Y., and Swanson, R. A. (2003). Astrocytes and brain injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.23:137–149. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

