Enhanced molecular analyses by combination of the HOPE-technique and laser microdissection
- PMID: 16759346
- PMCID: PMC1501060
- DOI: 10.1186/1746-1596-1-2
Enhanced molecular analyses by combination of the HOPE-technique and laser microdissection
Abstract
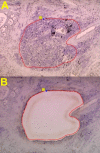
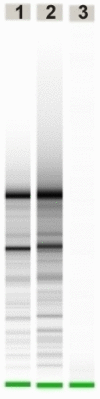
As part of an investigation aimed at illuminating the possibilities and limits of the HOPE-fixation and paraffin-embedding technique we here describe a novel procedure which was developed in order to combine the benefits of the HOPE-technique with the capabilities of laser microdissection. The presented procedure avoids the need for amplification of template-RNA thus facilitating reliable and reproducible results. The excellent preservation of nucleic acids, proteins, and morphology in HOPE-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues enhances the molecular applications available to date with materials acquired by laser microdissection when compared to formalin fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues, thus substantially extending the methodological panel in tissue based research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The HOPE technique opens up a multitude of new possibilities in pathology.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2006;47(1):15-9. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2006. PMID: 16838052 Review.
-
Tissue microarrays from HOPE-fixed specimens allow for enhanced high throughput molecular analyses in paraffin-embedded material.Pathol Res Pract. 2005;201(8-9):599-602. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2005.07.006. Pathol Res Pract. 2005. PMID: 16259114
-
HOPE-fixation enables improved PCR-based detection and differentiation of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in paraffin-embedded tissues.Pathol Res Pract. 2003;199(9):619-23. doi: 10.1078/0344-0338-00470. Pathol Res Pract. 2003. PMID: 14621198
-
Quantitative gene expression analysis in microdissected archival formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded tumor tissue.Am J Pathol. 2001 Feb;158(2):419-29. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63985-5. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11159180 Free PMC article.
-
Excavation of a buried treasure--DNA, mRNA, miRNA and protein analysis in formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissues.Histol Histopathol. 2011 Jun;26(6):797-810. doi: 10.14670/HH-26.797. Histol Histopathol. 2011. PMID: 21472693 Review.
Cited by
-
HOPE-BAL: improved molecular diagnostics by application of a novel technique for fixation and paraffin embedding.J Histochem Cytochem. 2011 Jun;59(6):601-14. doi: 10.1369/0022155411404417. Epub 2011 Mar 23. J Histochem Cytochem. 2011. PMID: 21430262 Free PMC article.
-
A novel human ex vivo model for the analysis of molecular events during lung cancer chemotherapy.Respir Res. 2007 Jun 14;8(1):43. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-8-43. Respir Res. 2007. PMID: 17567922 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of microRNA-497 and its prognostic significance in human breast cancer.Diagn Pathol. 2013 Oct 21;8:172. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-8-172. Diagn Pathol. 2013. Retraction in: Diagn Pathol. 2015 Mar 26;10:9. doi: 10.1186/s13000-015-0238-8. PMID: 24143964 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
KINFix--A formalin-free non-commercial fixative optimized for histological, immunohistochemical and molecular analyses of neurosurgical tissue specimens.Clin Neuropathol. 2016 Jan-Feb;35(1):3-12. doi: 10.5414/NP300907. Clin Neuropathol. 2016. PMID: 26521938 Free PMC article.
-
Photoreceptor cells display a daily rhythm in the orphan receptor Esrrβ.Mol Vis. 2015 Feb 19;21:173-84. eCollection 2015. Mol Vis. 2015. PMID: 25737630 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Droemann D, Goldmann T, Branscheid D, Clark R, Dalhoff K, Zabel P, Vollmer E. Toll-like Receptor 2 (TLR2) is expressed by alveolar type 2 cells and macrophages in the human lung. Histochem Cell Biol. 2003;119:103–108. - PubMed
-
- Goldmann T, Wiedorn KH, Kühl H, Olert J, Branscheid D, Pechkovsky D, Zissel G, Galle J, Müller-Quernheim J, Vollmer E. Assessment of transcriptional gene activity in situ by application of HOPE-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Pathol Res Pract. 2002;198:91–95. doi: 10.1078/0344-0338-00192. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

