Cadmium induces the expression of Grp78, an endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone, in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells
- PMID: 16759985
- PMCID: PMC1480533
- DOI: 10.1289/ehp.8920
Cadmium induces the expression of Grp78, an endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone, in LLC-PK1 renal epithelial cells
Abstract
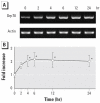
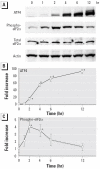
To reveal the effects of cadmium exposure on the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response, we examined the expression and function of 78-kDa glucose-regulated protein (Grp78) , an ER-resident molecular chaperone, in LLC-PK1 cells. In cells treated with 10 microM cadmium chloride, Grp78 protein levels increased after 6 hr and remained elevated at 24 hr. When cells were incubated with 1-20 microM CdCl2 for 6 hr, Grp78 increased in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, Grp78 mRNA levels were elevated in response to CdCl2 exposure. After exposure to 10 microM CdCl2, the levels of activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) were increased at 2 hr, with a further enhancement after that ; this accumulation followed the transient but marked phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 (eIF2(alpha)) on serine 51. Although ATF4 mRNA levels increased mildly by CdCl2 exposure, treatment with actinomycin D did not suppress CdCl2-induced accumulation of ATF4 protein, suggesting the involvement of posttranscriptional and, in part, transcriptional mechanisms. Compared with other heavy-metal compounds such as manganese chloride, zinc chloride, mercuric chloride, and lead chloride, CdCl2 could increase the levels of Grp78, ATF4, and the phosphorylated form of eIF2(alpha) more markedly without definite cellular damage. The silencing of Grp78 expression using short-interference RNA enhanced CdCl2-induced cellular damage. These results show that cadmium induces the expression of Grp78 probably via phosphorylation of eIF2(alpha) and resultant translation of ATF4, and this ER stress response plays a role in protection against cadmium cytotoxicity in this renal epithelial cell.
Figures





References
-
- Brostrom MA, Brostrom CO. Calcium dynamics and endoplasmic reticular function in the regulation of protein synthesis: implications for cell growth and adaptability. Cell Calcium. 2003;34:345–363. - PubMed
-
- Cigliano S, Remondelli P, Minichiello L, Mellone MC, Martire G, Bonatti S, et al. Analysis of metal-regulated metallo-thionein and heat shock gene expression in HeLa-derived cadmium-resistant cells. Exp Cell Res. 1996;228:173–180. - PubMed
-
- Croute F, Beau B, Murat J-C, Vincent C, Komatsu H, Obata F, et al. Expression of stress-related genes in a cadmium-resistant A549 human cell line. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 2005;68:703–718. - PubMed
-
- Elia G, De Marco A, Rossi A, Santoro MG. Inhibition of HSP70 expression by calcium ionophore A23187 in human cells. An effect independent of the acquisition of DNA-binding activity by the heat shock transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:16111–16118. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
