Uptake, tissue distribution, and excretion of brevetoxin-3 administered to mice by intratracheal instillation
- PMID: 16760139
- PMCID: PMC2652734
- DOI: 10.1080/15287390500360091
Uptake, tissue distribution, and excretion of brevetoxin-3 administered to mice by intratracheal instillation
Abstract
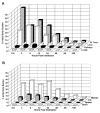
Brevetoxins are a family of potent lipid-soluble neurotoxins produced by the dinoflagellate Karenia brevis, the organism responsible for Florida red tide. Brevetoxins aerosolized by surf and wind produce irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat in people on or near red tide-affected beaches. The effects of chronic exposures to brevetoxins on healthy and health-compromised individuals are not known. The purpose of this study was to investigate the pulmonary uptake, tissue distribution, and excretion of polyether brevetoxin-3 in mice, a rodent model for investigating the potential systemic adverse health effects associated with repeated brevetoxin inhalation. Male CBA/CaJ mice were administered [3H]brevetoxin-3 by intratracheal instillation. Groups of 3 mice were sacrificed immediately after instillation and at 0.5, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 96 h postinstillation. Four additional mice were placed into metabolism cages for excreta collection up to 168 h postinstillation. Brevetoxin-3 distributed rapidly to all tissues, with the highest initial doses in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Elimination half-times ranged from approximately 28 h for fat, heart, intestines, kidneys, liver, and muscle to approximately 90 h for brain and testes. The total dose to tissue ranged from 39 ng brevetoxin equivalents-h/g for testes to 406 ng brevetoxin equivalents-h/g for liver. Approximately 90% of excretion had occurred within 96 h, with 11 and 64% of the initial brevetoxin dose excreted in urine and feces, respectively. These results are consistent with earlier reports of rapid absorption and widespread tissue distribution of brevetoxins in rats.
Figures
References
-
- Altshuler B, Pasternack B. Statistical measures of the lower limit of detection of a radioactivity counter. Health Phys. 1963;9:293–298. - PubMed
-
- Asai S, Krzanowski JJ, Anderson WH, Martin DF, Polson JB, Lockey RF, Bukantz SC, Szentivanyi A. Effects of toxin of red tide, Ptychodiscus brevis, on canine tracheal smooth muscle: A possible new asthma-triggering mechanism. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982;69:418–428. - PubMed
-
- Backer LC, Fleming LE, Rowan A, Cheng YS, Benson J, Pierce RH, Zaias J, Bean J, Bossart GD, Johnson D, Quimbo R, Baden DG. Recreational exposure to aerosolized brevetoxins during Florida red tide events. Harmful Algae. 2003;2:19–28. - PubMed
-
- Backer LC, Kirkpatrick B, Fleming LE, Cheng YC, Pierce R, Bean JA, Clark R, Johnson D, Wanner A, Tamer R, Zhou Y, Baden D. Occupational exposure to aerosolized brevetoxins during Florida red tide events: Effects on a healthy worker population. Environ Health Perspect. 2005;113(5):644–649. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benson JM, Tischler DL, Baden DG. Uptake, tissue distribution, and excretion of PbTx-3 administered to rats by intratracheal instillation. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 1999;57:345–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
