An autosomal recessive form of spastic cerebral palsy (CP) with microcephaly and mental retardation
- PMID: 16761294
- PMCID: PMC2573996
- DOI: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31288
An autosomal recessive form of spastic cerebral palsy (CP) with microcephaly and mental retardation
Abstract
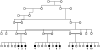
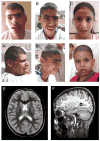
Cerebral palsy (CP) is defined as any nonprogressive motor deficits resulting from cerebral abnormalities that occur in the prenatal or perinatal period. Symptoms become apparent during the first year of life. Genetic forms of CP account for about 2% in European populations but are thought to cause a substantial proportion in consanguineous families. We have identified a large consanguineous family from Oman with spastic diplegia, microcephaly, and mental retardation. Additional manifestations include hyperreflexia, clumsiness, unstable gait, drooling, and dysarthria. There was phenotypic variability among different individuals, but spastic diplegia, microcephaly, and mental retardation were three constant traits present in all affected individuals.
Copyright 2006 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Linkage studies with the gene for an X-linked syndrome of mental retardation, microcephaly and spastic diplegia (MRX2).Am J Med Genet. 1988 May-Jun;30(1-2):493-508. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320300152. Am J Med Genet. 1988. PMID: 3177467
-
Adaptor protein complex-4 (AP-4) deficiency causes a novel autosomal recessive cerebral palsy syndrome with microcephaly and intellectual disability.J Med Genet. 2011 Feb;48(2):141-4. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2010.082263. Epub 2010 Oct 23. J Med Genet. 2011. PMID: 20972249 Free PMC article.
-
The syndrome of retinal pigmentary degeneration, microcephaly, and severe mental retardation (Mirhosseini-Holmes-Walton syndrome): report of two patients.Am J Med Genet. 1985 Oct;22(2):223-8. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320220202. Am J Med Genet. 1985. PMID: 4050854
-
Filippi syndrome: a new case with skeletal abnormalities.J Med Genet. 1995 Aug;32(8):659-61. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.8.659. J Med Genet. 1995. PMID: 7473664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DYRK1A pathogenic variants in two patients with syndromic intellectual disability and a review of the literature.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Dec;8(12):e1544. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1544. Epub 2020 Nov 7. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 33159716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Increasing prevalence of cerebral palsy among children and adolescents in China 1988-2020: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Rehabil Med. 2021 May 24;53(5):jrm00195. doi: 10.2340/16501977-2841. J Rehabil Med. 2021. PMID: 33961057 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-exome sequencing points to considerable genetic heterogeneity of cerebral palsy.Mol Psychiatry. 2015 Feb;20(2):176-82. doi: 10.1038/mp.2014.189. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Mol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25666757
-
Case report: Suspecting guanine nucleotide-binding protein beta 1 mutation in dyskinetic cerebral palsy is important.Front Pediatr. 2023 Oct 13;11:1204360. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1204360. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37900673 Free PMC article.
-
Exome Analysis Identified Novel Homozygous Splice Site Donor Alteration in NT5C2 Gene in a Saudi Family Associated With Spastic Diplegia Cerebral Palsy, Developmental Delay, and Intellectual Disability.Front Genet. 2020 Feb 21;11:14. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00014. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32153630 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in mitochondrial enzyme GPT2 cause metabolic dysfunction and neurological disease with developmental and progressive features.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Sep 20;113(38):E5598-607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609221113. Epub 2016 Sep 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27601654 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adler E. Familial cerebral palsy. J Chronic Dis. 1961;13:207–214. - PubMed
-
- Al-Rajeh S, Bademosi O, Awada A, Ismail H, Al-Shammasi S, Dawodu A. Cerebral palsy in Saudi Arabia: a case-control study of risk factors. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1991;33:1048–1052. - PubMed
-
- Blair E, Stanley Fj. Intrapartum asphyxia: a rare cause of cerebral palsy. J Pediatr. 1988;112:515–519. - PubMed
-
- Böök Ja. A genetic and neuropsychiatric investigation of a North-Swedish population with special regard to schizophrenia and mental deficiency. II. Mental deficiency and convulsive disorders. Acta Genet Stat Med. 1953;4:345–414. - PubMed
-
- Bundey S, Alam H. A five-year prospective study of the health of children in different ethnic groups, with particular reference to the effect of inbreeding. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1:206–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

