Quantitative EEG and effect of hypothermia on brain recovery after cardiac arrest
- PMID: 16761828
- PMCID: PMC3050568
- DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2006.873394
Quantitative EEG and effect of hypothermia on brain recovery after cardiac arrest
Abstract
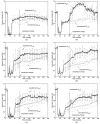
In this paper, we provide a quantitative electroencephalogram (EEG) analysis to study the effect of hypothermia on the neurological recovery of brain after cardiac arrest. We hypothesize that the brain injury results in a reduction in information of the brain rhythm. To measure the information content of the EEG a new measure called information quantity (IQ), which is the Shannon entropy of decorrelated EEG signals, is developed. For decorrelating EEG signals, we use the discrete wavelet transform (DWT) which is known to have good decorrelating properties and to show a good match to the standard clinical bands in EEG. In measuring the amount of information, IQ shows better tracking capability for dynamic amplitude change and frequency component change than conventional entropy-based measures. Experiments are carried out in rodents (n = 30) to monitor the neurological recovery after cardiac arrest. In addition, EEG signal recovery under normothermic (37 degrees C) and hypothermic (33 degrees C) resuscitation following 5, 7, and 9 min of cardiac arrest is recorded and analyzed. Experimental results show that the IQ is greater for hypothermic than normothermic rats, with an IQ difference of more than 0.20 (0.20 +/- 0.11 is 95% condidence interval). The results quantitatively support the hypothesis that hypothermia accelerates the electrical recovery from brain injury after cardiac arrest.
Figures



References
-
- Thakor NV, Tong S. Advances in quantitative electroencephalogram analysis methods. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2004;6:453–495. - PubMed
-
- Tong S, Bezerianos A, Malhotra A, Zhu Y, Thakor NV. Parameterized entropy analysis of EEG following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Phys. Lett. A. 2003;314:354–361.
-
- Bezerianos A, Tong S, Thakor NV. Time-dependent entropy estimation of EEG rhythm changes following brain ischemia. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2003;31:221–232. - PubMed
-
- Tong S, Bezerianos A, Paul J, Zhu Y, Thakor NV. Nonextensive entropy measure of EEG following brain injury from cardiac arrest. Physica A. 2002;305:619–628.
-
- Rosso OA, Blanco S, Yordanova J, Kolev V, Figliola A, Schürmann M, Başar E. Wavelet entropy: a new tool for analysis of short duration brain electrical signals. J. Neurosci. Meth. 2001;105:65–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

