The effect of RGD fluorosurfactant polymer modification of ePTFE on endothelial cell adhesion, growth, and function
- PMID: 16762410
- PMCID: PMC2048534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.05.009
The effect of RGD fluorosurfactant polymer modification of ePTFE on endothelial cell adhesion, growth, and function
Abstract
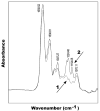
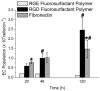
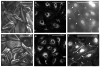
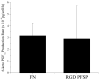
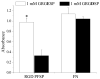
We have synthesized and characterized a novel peptide fluorosurfactant polymer (PFSP) modification that facilitates the adhesion and growth of endothelial cells on expanded polytetrafluoroetheylene (ePTFE) vascular graft material. This PFSP consists of a poly(vinyl amine) (PVAm) backbone with integrin binding Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) peptides and perfluorocarbon pendant branches for adsorption and stable adhesion to underlying ePTFE. Aqueous PFSP solution was used to modify the surface of fluorocarbon substrates. Following subconfluent seeding, endothelial cell (EC) adhesion and growth on PFSP was assessed by determining cell population at different time points. Spectroscopic results indicated successful synthesis of PFSP. PFSP modification of ePTFE reduced the receding water contact angle measurement from 120 degrees to 6 degrees , indicating successful surface modification. Quantification of cell population demonstrated reduced EC attachment efficiency but increased growth rate on RGD PFSP compared with fibronectin (FN). Actin staining revealed a well-developed cytoskeleton for ECs on RGD PFSP indicative of stable adhesion. Uptake of acetylated low-density lipoprotein and positive staining for VE-Cadherin confirm EC phenotype for adherent cells. Production of prostacyclin, a potent antiplatelet agent, was equivalent between ECs on FN and RGD PFSP surfaces. Our results indicate successful synthesis and surface modification with PFSP; this is a simple, quantitative, and effective approach to modifying ePTFE to encourage endothelial cell attachment, growth, and function.
Figures


References
-
- Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics. [cited 2005 August 9]. 2005 Update. 2004 Available from: http://www.americanheart.org/presenter.jhtml?identifier=1928.
-
- Sayers RD, Raptis S, Berce M, Miller JH. Long-term results of femorotibial bypass with vein or polytetrafluoroethylene. Br J Surg. 1998 Jul;85(7):934–8. - PubMed
-
- Faries PL, Logerfo FW, Arora S, Hook S, Pulling MC, Akbari CM, et al. A comparative study of alternative conduits for lower extremity revascularization: all-autogenous conduit versus prosthetic grafts. J Vasc Surg. 2000 Dec;32(6):1080–90. - PubMed
-
- Cines DB, Pollak ES, Buck CA, Loscalzo J, Zimmerman GA, McEver RP, et al. Endothelial cells in physiology and in the pathophysiology of vascular disorders. Blood. 1998 May 15;91(10):3527–61. - PubMed
-
- Colman RW. Hemostasis and thrombosis : basic principles and clinical practice. 4. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2000.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

