Dietary exposure of largemouth bass to OCPs changes expression of genes important for reproduction
- PMID: 16765462
- PMCID: PMC1892580
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.05.003
Dietary exposure of largemouth bass to OCPs changes expression of genes important for reproduction
Abstract
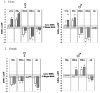
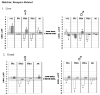
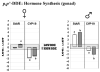
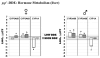
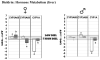
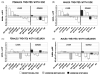
Dieldrin and p,p'-DDE are ubiquitous contaminants known to act as endocrine disruptors, causing impaired development and reproduction in fish and wildlife. In order to elucidate the mechanisms by which dieldrin and p,p'-DDE cause endocrine disruption in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides), fish were exposed subchronically through the diet to both contaminants. Following 120 days of exposure, p,p'-DDE decreased estradiol in females, but increased 11-ketotestosterone in both sexes. Dieldrin on the other hand, decreased estradiol and 11-ketotestosterone in both sexes. Both pesticides also altered steady state mRNA expression levels of a set of genes chosen to represent three possible mechanisms of endocrine disruption: (1) direct interaction with soluble sex steroid receptors, (2) biosynthesis of endogenous sex hormones, and (3) metabolism of endogenous hormones. p,p'-DDE acted as a weak estrogen, increasing the expression of vitellogenin and estrogen receptor alpha in the liver. p,p'-DDE also altered the expression of genes involved in the synthesis of endogenous hormones as well as their metabolism. Dieldrin, on the other hand, only altered expression of vitellogenin and not estrogen receptor alpha. Dieldrin also altered the expression of genes involved in hormone synthesis and metabolism, and it dramatically lowered plasma hormone levels. Both pesticides targeted expression of genes involved in all three modes of action, suggesting that they each have multiple modes of action.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Organochlorine pesticides: Agrochemicals with potent endocrine-disrupting properties in fish.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 May 1;507:110764. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110764. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32112812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to p,p'-DDE or dieldrin during the reproductive season alters hepatic CYP expression in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides).Aquat Toxicol. 2007 Feb 15;81(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.10.008. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Aquat Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17145087 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling of gene expression pattern alteration by p,p'-DDE and dieldrin in largemouth bass.Mar Environ Res. 2006 Jul;62 Suppl(Suppl):S415-9. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2006.04.049. Epub 2006 Apr 18. Mar Environ Res. 2006. PMID: 16707152 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional networks associated with the immune system are disrupted by organochlorine pesticides in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) ovary.Aquat Toxicol. 2016 Aug;177:405-16. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.06.009. Epub 2016 Jun 17. Aquat Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27391359
-
Methylmercury-induced changes in gene transcription associated with neuroendocrine disruption in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides).Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014 Jul 1;203:215-224. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2014.03.029. Epub 2014 Mar 30. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24694518 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Organochlorine pesticides: Agrochemicals with potent endocrine-disrupting properties in fish.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020 May 1;507:110764. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2020.110764. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32112812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Site-specific impacts on gene expression and behavior in fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) exposed in situ to streams adjacent to sewage treatment plants.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Oct 8;10 Suppl 11(Suppl 11):S11. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-S11-S11. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19811676 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and transcriptional modulation of the largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides, vitellogenin receptor during oocyte development by insulin and sex steroids.Biol Reprod. 2012 Sep 21;87(3):67. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.099812. Print 2012 Sep. Biol Reprod. 2012. PMID: 22786822 Free PMC article.
-
Sexually dimorphic transcriptomic responses in the teleostean hypothalamus: a case study with the organochlorine pesticide dieldrin.Neurotoxicology. 2013 Jan;34:105-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.09.012. Epub 2012 Oct 3. Neurotoxicology. 2013. PMID: 23041725 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to p,p'-DDE or dieldrin during the reproductive season alters hepatic CYP expression in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides).Aquat Toxicol. 2007 Feb 15;81(1):27-35. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2006.10.008. Epub 2006 Nov 10. Aquat Toxicol. 2007. PMID: 17145087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen HR, Vinggaard AM, Rasmussen TH, Gjermandsen IM, Bonefeld-Jorgensen EC. Effects of currently used pesticides in assays for estrogenicity, androgenicity, and aromatase activity in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2002;179:1–12. - PubMed
-
- Arukwe A, Förlin L, Goksøyr A. Xenobiotic and steroid biotransformation enzymes in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) liver treated with an estrogenic compound: 4-nonylphenol. Environ Toxicol Chem. 1997;16:2576–2583.
-
- Arukwe A. Cellular and molecular responses to endocrine-modulators and the impact on fish reproduction. Mar Pollut Bull. 2001;42:643–655. - PubMed
-
- Attia GR, Dooley CA, Rainey WE, Carr BR. Transforming growth factor beta inhibits steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein expression in human ovarian thecal cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2000;170:123–129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

