Analysis of the subcellular localization, function, and proteolytic control of the Arabidopsis cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor ICK1/KRP1
- PMID: 16766674
- PMCID: PMC1533933
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.106.081406
Analysis of the subcellular localization, function, and proteolytic control of the Arabidopsis cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor ICK1/KRP1
Abstract
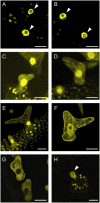
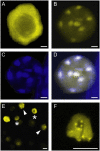
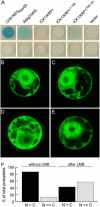
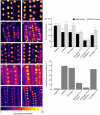
Recent studies have shown that cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors can have a tremendous impact on cell cycle progression in plants. In animals, CDK inhibitors are tightly regulated, especially by posttranslational mechanisms of which control of nuclear access and regulation of protein turnover are particularly important. Here we address the posttranslational regulation of INHIBITOR/INTERACTOR OF CDK 1 (ICK1)/KIP RELATED PROTEIN 1 (KRP1), an Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) CDK inhibitor. We show that ICK1/KRP1 exerts its function in the nucleus and its presence in the nucleus is controlled by multiple nuclear localization signals as well as by nuclear export. In addition, we show that ICK1/KRP1 localizes to different subnuclear domains, i.e. in the nucleoplasm and to the chromocenters, hinting at specific actions within the nuclear compartment. Localization to the chromocenters is mediated by an N-terminal domain, in addition we find that this domain may be involved in cyclin binding. Further we demonstrate that ICK1/KRP1 is an unstable protein and degraded by the 26S proteasome in the nucleus. This degradation is mediated by at least two domains indicating the presence of at least two different pathways impinging on ICK1/KRP1 protein stability.
Figures



References
-
- Bisbis B, Delmas F, Joubes J, Sicard A, Hernould M, Inze D, Mouras A, Chevalier C (2006) Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors regulate the CDK/cyclin complex activities in endoreduplicating cells of developing tomato fruit. J Biol Chem 281: 7374–7383 - PubMed
-
- Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A, Pagano M (1999) SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol 1: 193–199 - PubMed
-
- Chan GK, Liu ST, Yen TJ (2005) Kinetochore structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 15: 589–598 - PubMed
-
- Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16: 735–743 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

