Effective treatment of manganese-induced occupational Parkinsonism with p-aminosalicylic acid: a case of 17-year follow-up study
- PMID: 16766929
- PMCID: PMC4180660
- DOI: 10.1097/01.jom.0000204114.01893.3e
Effective treatment of manganese-induced occupational Parkinsonism with p-aminosalicylic acid: a case of 17-year follow-up study
Abstract
Objective: Chronic manganese (Mn) intoxication induces syndromes resembling Parkinson disease. The clinical intervention has largely been unsuccessful. We report a 17-year follow-up study of effective treatment of occupational Mn parkinsonism with sodium para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS).
Methods: The patient, female and aged 50 at the time of treatment, was exposed to airborne Mn for 21 years (1963-1984). The patient had palpitations, hand tremor, lower limb myalgia, hypermyotonia, and a distinct festinating gait. She received 6 g PAS per day through an intravenous drip infusion for 4 days and rested for 3 days as one therapeutic course. Fifteen such courses were carried out between March and June 1987.
Results: At the end of PAS treatment, her symptoms were significantly alleviated, and handwriting recovered to normal. Recent follow-up examination at age 67 years (in 2004) showed a general normal presentation in clinical, neurologic, brain magnetic resonance imaging, and handwriting examinations with a minor yet passable gait.
Conclusions: This case study suggests that PAS appears to be an effective drug for treatment of severe chronic Mn poisoning with a promising prognosis.
Figures

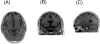
References
-
- Olanow CW. Manganese-induced parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1012:209–223. - PubMed
-
- Ono K, Komai K, Yamada M. Myoclonic involuntary movement associated with chronic manganese poisoning. J Neurol Sci. 2002;199:93–96. - PubMed
-
- Pal PK, Samii A, Calne DB. Manganese neurotoxicity: a review of clinical features, imaging and pathology. Neurotoxicology. 1999;20:227–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

