Bone morphogenetic protein signaling and growth suppression in colon cancer
- PMID: 16769811
- PMCID: PMC4138725
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00482.2005
Bone morphogenetic protein signaling and growth suppression in colon cancer
Abstract
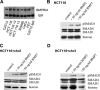
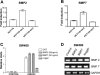
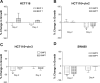
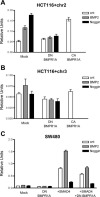
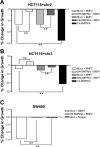
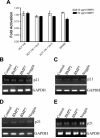
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are members of the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily, which utilize BMP receptors and intracellular SMADs to transduce their signals to regulate cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis. Because mutations in BMP receptor type IA (BMPRIA) and SMAD4 are found in the germline of patients with the colon cancer predisposition syndrome juvenile polyposis, and because the contribution of BMP in colon cancers is largely unknown, we examined colon cancer cells and tissues for evidence of BMP signaling and determined its growth effects. We determined the presence and functionality of BMPR1A by examining BMP-induced phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of SMAD1; transcriptional activity via a BMP-specific luciferase reporter; and growth characteristics by cell cycle analysis, cell growth, and 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide metabolic assays. These assays were also performed after transfection with a dominant negative (DN) BMPR1A construct. In SMAD4-null SW480 cells, we examined BMP effects on cellular wound assays as well as BMP-induced transcription in the presence of transfected SMAD4. We also determined the expression of BMPR1A, BMP ligands, and phospho-SMAD1 in primary human colon cancer specimens. We found intact BMP signaling and modest growth suppression in HCT116 and two derivative cell lines and, surprisingly, growth suppression in SMAD4-null SW480 cells. BMP-induced SMAD signaling and BMPR1A-mediated growth suppression were reversed with DN BMPR1A transfection. BMP2 slowed wound closure, and transfection of SMAD4 into SW480 cells did not change BMP-specific transcriptional activity over controls due to receptor stimulation by endogenously produced ligand. We found no cell cycle alterations with BMP treatment in the HCT116 and derivative cell lines, but there was an increased G1 fraction in SW480 cells that was not due to increased p21 transcription. In human colon cancer specimens, BMP2 and BMP7 ligands, BMPRIA, and phospho-SMAD1 were expressed. In conclusion, BMP signaling is intact and growth suppressive in human colon cancer cells. In addition to SMADs, BMP may utilize SMAD4-independent pathways for growth suppression in colon cancers.
Figures



References
-
- Arnold SF, Tims E, McGrath BE. Identification of bone morpho-genetic proteins and their receptors in human breast cancer cell lines: importance of BMP2. Cytokine. 1999;11:1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Balemans W, Van Hul W. Extracellular regulation of BMP signaling in vertebrates: a cocktail of modulators. Dev Biol. 2002;250:231–250. - PubMed
-
- Brubaker KD, Corey E, Brown LG, Vessella RL. Bone morpho-genetic protein signaling in prostate cancer cell lines. J Cell Biochem. 2004;91:151–160. - PubMed
-
- Carethers JM. Biology of colorectal carcinoma. In: Rustgi A, Crawford J, editors. Gastrointestinal Cancers: Biology and Clinical Management. 1st ed. Saunders; Philadelphia, PA: 2003. pp. 407–419.
-
- Carethers JM, Pham TT. Mutations of transforming growth factor beta 1 type II receptor, BAX, and insulin-like growth factor II receptor genes in microsatellite unstable cell lines. In Vivo. 2000;14:13–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

