Activation and dramatically increased cytolytic activity of tumor specific T lymphocytes after radio-frequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal liver metastases
- PMID: 16773688
- PMCID: PMC4087464
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i23.3716
Activation and dramatically increased cytolytic activity of tumor specific T lymphocytes after radio-frequency ablation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and colorectal liver metastases
Abstract
Aim: To assess if a specific cytotoxic T cell response can be induced in patients with malignant liver tumors treated with radio-frequency ablation (RFA).
Methods: Six Patients with liver metastases of colorectal cancer and 6 with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) underwent RFA. Blood was sampled before, 4 and 8 wk after RFA. Test antigens were autologous liver and tumor lysate obtained from each patient by biopsy. Peripheral T cell activation was assessed by an interferon gamma (IFNgamma) secretion assay and flow cytometry. T cells were double-stained for CD4/CD8 and IFNgamma to detect cytotoxic T cells. The ratio of IFNgamma positive and IFNgamma negative T cells was determined as the stimulation index (SI). To assess cytolytic activity, T cells were co-incubated with human CaCo colorectal cancer and HepG2 HCC cells and release of cytosolic adenylate kinase was measured by a luciferase assay.
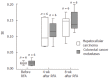
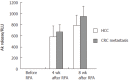
Results: Before RFA SI was 0.021 (+/- 0.006) for CD4(+) and 0.022 (+/- 0.004) for CD8(+) T cells against nonmalignant liver tissue and 0.018 (+/- 0.005) for CD4(+) and 0.021 (+/- 0.004) for CD8(+) cells against autologous tumor tissue. Four weeks after RFA SI against tumor tissue increased to 0.109 (+/- 0.005) for CD4(+) and 0.11 (+/- 0.012) for CD8(+) T cells against HCC, and to 0.115 (+/- 0.031) for CD4(+) and 0.15 (+/- 0.02) for CD8(+) cells for colorectal metastases (P < 0.0001). No increased SI was observed with nonmalignant tumor tissue at all time points. Before RFA cytolytic activity against the respective cancer cells was low with 2.62 (+/- 0.37) relative luminescence units (RLU), but rose more than 100 fold 4 and 8 wk after RFA. Spontaneous release was < 2% of maximum release in all experiments.
Conclusion: Patients with primary and secondary tumors of the liver show a significant tumor-specific cytotoxic T-cell stimulation with a dramatically increased tumor specific cytolytic activity of CD8(+) T cells after RFA.
Figures

References
-
- Solbiati L, Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Ierace T, Meloni F, Dellanoce M, Cova L, Halpern EF, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of hepatic metastases from colorectal cancer: long-term results in 117 patients. Radiology. 2001;221:159–166. - PubMed
-
- Vogl TJ, Straub R, Eichler K, Woitaschek D, Mack MG. Malignant liver tumors treated with MR imaging-guided laser-induced thermotherapy: experience with complications in 899 patients (2,520 lesions) Radiology. 2002;225:367–377. - PubMed
-
- Mack MG, Straub R, Eichler K, Engelmann K, Zangos S, Roggan A, Woitaschek D, Böttger M, Vogl TJ. Percutaneous MR imaging-guided laser-induced thermotherapy of hepatic metastases. Abdom Imaging. 2001;26:369–374. - PubMed
-
- Hänsler J, Neureiter D, Strobel D, Müller W, Mutter D, Bernatik T, Hahn EG, Becker D. Cellular and vascular reactions in the liver to radio-frequency thermo-ablation with wet needle applicators. Study on juvenile domestic pigs. Eur Surg Res. 2002;34:357–363. - PubMed
-
- Wissniowski TT, Hänsler J, Neureiter D, Frieser M, Schaber S, Esslinger B, Voll R, Strobel D, Hahn EG, Schuppan D. Activation of tumor-specific T lymphocytes by radio-frequency ablation of the VX2 hepatoma in rabbits. Cancer Res. 2003;63:6496–6500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

