Gab1 is required for cell cycle transition, cell proliferation, and transformation induced by an oncogenic met receptor
- PMID: 16775003
- PMCID: PMC1556377
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-03-0244
Gab1 is required for cell cycle transition, cell proliferation, and transformation induced by an oncogenic met receptor
Abstract
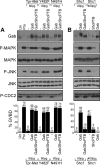
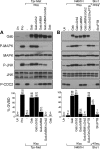
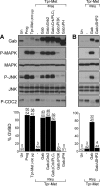
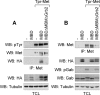
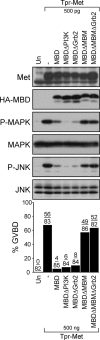
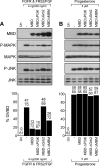
We have shown previously that either Grb2- or Shc-mediated signaling from the oncogenic Met receptor Tpr-Met is sufficient to trigger cell cycle progression in Xenopus oocytes. However, direct binding of these adaptors to Tpr-Met is dispensable, implying that another Met binding partner mediates these responses. In this study, we show that overexpression of Grb2-associated binder 1 (Gab1) promotes cell cycle progression when Tpr-Met is expressed at suboptimal levels. This response requires that Gab1 possess an intact Met-binding motif, the pleckstrin homology domain, and the binding sites for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and tyrosine phosphatase SHP-2, but not the Grb2 and CrkII/phospholipase Cgamma binding sites. Importantly, we establish that Gab1-mediated signals are critical for cell cycle transition promoted by the oncogenic Met and fibroblast growth factor receptors, but not by progesterone, the natural inducer of cell cycle transition in Xenopus oocytes. Moreover, Gab1 is essential for Tpr-Met-mediated morphological transformation and proliferation of fibroblasts. This study provides the first evidence that Gab1 is a key binding partner of the Met receptor for induction of cell cycle progression, proliferation, and oncogenic morphological transformation. This study identifies Gab1 and its associated signaling partners as potential therapeutic targets to impair proliferation or transformation of cancer cells in human malignancies harboring a deregulated Met receptor.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oncogenic Met receptor induces cell-cycle progression in Xenopus oocytes independent of direct Grb2 and Shc binding or Mos synthesis, but requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Raf signaling.J Cell Physiol. 2006 Apr;207(1):271-85. doi: 10.1002/jcp.20564. J Cell Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16331688
-
Role of the Grb2-associated binder 1/SHP-2 interaction in cell growth and transformation.Cancer Res. 2004 Mar 15;64(6):2007-15. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2886. Cancer Res. 2004. PMID: 15026337
-
Coupling of Gab1 to c-Met, Grb2, and Shp2 mediates biological responses.J Cell Biol. 2000 Jun 26;149(7):1419-32. doi: 10.1083/jcb.149.7.1419. J Cell Biol. 2000. PMID: 10871282 Free PMC article.
-
Gab1, SHP-2 and other novel regulators of Ras: targets for anticancer drug discovery?Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003 Jun;3(3):177-92. doi: 10.2174/1568009033481976. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2003. PMID: 12769687 Review.
-
Met, metastasis, motility and more.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003 Dec;4(12):915-25. doi: 10.1038/nrm1261. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003. PMID: 14685170 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
PAK4, a target of miR-9-5p, promotes cell proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in colorectal cancer.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019 Nov 8;24:58. doi: 10.1186/s11658-019-0182-9. eCollection 2019. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2019. Retraction in: Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2025 Apr 16;30(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s11658-025-00730-w. PMID: 31728150 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Cholinergic Grb2-Associated-Binding Protein 1 Regulates Cognitive Function.Cereb Cortex. 2018 Jul 1;28(7):2391-2404. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx141. Cereb Cortex. 2018. PMID: 28591834 Free PMC article.
-
Met receptor-induced Grb2 or Shc signals both promote transformation of intestinal epithelial cells, albeit they are required for distinct oncogenic functions.BMC Cancer. 2014 Apr 4;14:240. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-240. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24708867 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct requirements for Gab1 in Met and EGF receptor signaling in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Sep 25;104(39):15376-81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702555104. Epub 2007 Sep 19. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17881575 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant MET Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling in Glioblastoma: Targeted Therapy and Future Directions.Cells. 2024 Jan 25;13(3):218. doi: 10.3390/cells13030218. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38334610 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bardelli A., Basile M. L., Audero E., Giordano S., Wennstrom S., Menard S., Comoglio P. M., Ponzetto C. Concomitant activation of pathways downstream of Grb2 and PI 3-kinase is required for MET-mediated metastasis. Oncogene. 1999;18:1139–1146. - PubMed
-
- Bardelli A., Longati P., Gramaglia D., Stella M. C., Comoglio P. M. Gab1 coupling to the HGF/Met receptor multifunctional docking site requires binding of Grb2 and correlates with the transforming potential. Oncogene. 1997;15:3103–3111. - PubMed
-
- Birchmeier C., Birchmeier W., Gherardi E., Vande Woude G. F. Met, metastasis, motility and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2003;4:915–925. - PubMed
-
- Bladt F., Riethmacher D., Isenmann S., Aguzzi A., Birchmeier C. Essential role for the c-met receptor in the migration of myogenic precursor cells into the limb bud. Nature. 1995;376:768–771. - PubMed
-
- Browaeys-Poly E., Cailliau K., Vilain J. P. Signal transduction pathways triggered by fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes after fibroblast growth factor 1 addition. Role of Grb2, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Src tyrosine kinase, and phospholipase Cgamma. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000;267:6256–6263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

