MARK2/EMK1/Par-1Balpha phosphorylation of Rab11-family interacting protein 2 is necessary for the timely establishment of polarity in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
- PMID: 16775013
- PMCID: PMC1525241
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-08-0736
MARK2/EMK1/Par-1Balpha phosphorylation of Rab11-family interacting protein 2 is necessary for the timely establishment of polarity in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells
Abstract
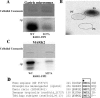
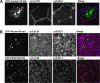
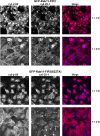
Rab11a, myosin Vb, and the Rab11-family interacting protein 2 (FIP2) regulate plasma membrane recycling in epithelial cells. This study sought to characterize more fully Rab11-FIP2 function by identifying kinase activities modifying Rab11-FIP2. We have found that gastric microsomal membrane extracts phosphorylate Rab11-FIP2 on serine 227. We identified the kinase that phosphorylated Rab11-FIP2 as MARK2/EMK1/Par-1Balpha (MARK2), and recombinant MARK2 phosphorylated Rab11-FIP2 only on serine 227. We created stable Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell lines expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein-Rab11-FIP2 wild type or a nonphosphorylatable mutant [Rab11-FIP2(S227A)]. Analysis of these cell lines demonstrates a new role for Rab11-FIP2 in addition to that in the plasma membrane recycling system. In calcium switch assays, cells expressing Rab11-FIP2(S227A) showed a defect in the timely reestablishment of p120-containing junctional complexes. However, Rab11-FIP2(S227A) did not affect localization with recycling system components or the normal function of apical recycling and transcytosis pathways. These results indicate that phosphorylation of Rab11-FIP2 on serine 227 by MARK2 regulates an alternative pathway modulating the establishment of epithelial polarity.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Rab11-FIP2 interaction with MYO5B regulates movement of Rab11a-containing recycling vesicles.Traffic. 2014 Mar;15(3):292-308. doi: 10.1111/tra.12146. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 24372966 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of Rab11-FIP2 regulates polarity in MDCK cells.Mol Biol Cell. 2012 Jun;23(12):2302-18. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-08-0681. Epub 2012 May 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2012. PMID: 22553350 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11 family interacting protein 2 associates with Myosin Vb and regulates plasma membrane recycling.J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 27;277(52):50415-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M209270200. Epub 2002 Oct 21. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 12393859
-
Interaction of phosphorylated Rab11-FIP2 with Eps15 regulates apical junction composition.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Apr 15;28(8):1088-1100. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E16-04-0214. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28228550 Free PMC article.
-
Apical surface formation in MDCK cells: regulation by the serine/threonine kinase EMK1.Methods. 2003 Jul;30(3):269-76. doi: 10.1016/s1046-2023(03)00033-1. Methods. 2003. PMID: 12798141 Review.
Cited by
-
Rab11-FIP1 phosphorylation by MARK2 regulates polarity in MDCK cells.Cell Logist. 2017 Jan 9;7(1):e1271498. doi: 10.1080/21592799.2016.1271498. eCollection 2017. Cell Logist. 2017. PMID: 28396819 Free PMC article.
-
Genes regulating membrane-associated E-cadherin and proliferation in adenomatous polyposis coli mutant colon cancer cells: High content siRNA screen.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 15;15(10):e0240746. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240746. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33057364 Free PMC article.
-
Rab11-FIP2 interaction with MYO5B regulates movement of Rab11a-containing recycling vesicles.Traffic. 2014 Mar;15(3):292-308. doi: 10.1111/tra.12146. Epub 2014 Jan 22. Traffic. 2014. PMID: 24372966 Free PMC article.
-
MARK3-mediated phosphorylation of ARHGEF2 couples microtubules to the actin cytoskeleton to establish cell polarity.Sci Signal. 2017 Oct 31;10(503):eaan3286. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aan3286. Sci Signal. 2017. PMID: 29089450 Free PMC article.
-
Recycling Endosomes and Viral Infection.Viruses. 2016 Mar 8;8(3):64. doi: 10.3390/v8030064. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27005655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bohm H., Brinkmann V., Drab M., Henske A., Kurzchalia T. V. Mammalian homologues of C. elegans PAR-1 are asymmetrically localized in epithelial cells and may influence their polarity. Curr. Biol. 1997;7:603–606. - PubMed
-
- Breitfeld P. P., Casanova J. E., Harris J. M., Simister N. E., Mostov K. E. Expression and analysis of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells using retroviral vectors. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:329–337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA-68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-58404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK048370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-43405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK051970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK043405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK058404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-20593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 HD015052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020593/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK-48370/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HD15052/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK-51970/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

