HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain
- PMID: 16775128
- PMCID: PMC6674036
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3815-05.2006
HMGB1, a novel cytokine-like mediator linking acute neuronal death and delayed neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain
Abstract
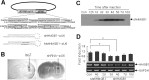
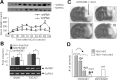
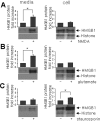
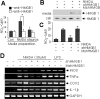
Cerebral ischemic injury proceeds with excitotoxicity-induced acute neuronal death in the ischemic core and with delayed damage processes in the penumbra. However, knowledge concerning the direct mediators that connect these two processes is limited. Here, we demonstrate that high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), a nonhistone DNA-binding protein, is massively released into the extracellular space immediately after ischemic insult and that it subsequently induces neuroinflammation in the postischemic brain. Short hairpin (sh)RNA-mediated HMGB1 downregulation in the postischemic brain suppressed infarct size, microglia activation, and proinflammatory marker induction, indicating that HMGB1 plays a crucial role in the inflammatory process. The proinflammatory cytokine-like function of extracellular HMGB1 was further verified in primary cortical cultures and microglial cultures. HMGB1 was found to accumulate in NMDA-treated primary cortical culture media, and supernatants collected from these cultures were found to trigger microglia activation, the hallmark of brain inflammation. Moreover, treatment with recombinant HMGB1 also induced microglial activation, but HMGB1-depleted supernatant produced by anti-HMGB1 antibody treatment or by HMGB1 shRNA expression did not, thus demonstrating the essential role of HMGB1 in microglial activation. Together, these results indicate that HMGB1 functions as a novel proinflammatory cytokine-like factor that connects excitotoxicity-induced acute damage processes and delayed inflammatory processes in the postischemic brain.
Figures


References
-
- Abe K, Aoki M, Kawagoe J, Yoshida T, Hattori A, Kogure K, Itoyama Y (1995). Ischemic delayed neuronal death. A mitochondrial hypothesis. Stroke 26:1478–1489. - PubMed
-
- Abraham E, Arcaroli J, Carmody A, Wang H, Tracey KJ (2000). HMG-1 as a mediator of acute lung inflammation. J Immunol 165:2950–2954. - PubMed
-
- Agnello D, Wang H, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Ghezzi P (2002). HMGB-1, a DNA-binding protein with cytokine activity, induces brain TNF and IL-6 production, and mediates anorexia and taste aversion. Cytokine 18:231–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
