MR imaging features of brain stem hypoplasia in familial horizontal gaze palsy and scoliosis
- PMID: 16775302
- PMCID: PMC8133918
MR imaging features of brain stem hypoplasia in familial horizontal gaze palsy and scoliosis
Abstract
We report the case of a child with horizontal gaze palsy, pendular nystagmus, and discrete thoracolumbar scoliosis. MR imaging of the brain depicted pons hypoplasia with an absence of the facial colliculi, hypoplasia, butterfly configuration of the medulla, and the presence of a deep midline pontine cleft (split pons sign). These MR imaging findings suggest familial horizontal gaze palsy with progressive kyphoscoliosis, a rare congenital disorder. To the best of our knowledge, MR imaging findings of only 4 similar cases, with or without progressive idiopathic scoliosis, have been reported. We discuss the pathogenesis substratum of this entity. Early recognition of this rare entity is important if supportive therapeutic measures in progressive scoliosis are to be applied.
Figures
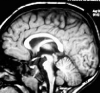
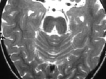
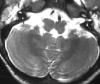

Comment in
-
Mutation in ROBO3 gene recently demonstrated in patients with horizontal gaze palsy with progressive scoliosis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007 Feb;28(2):198. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007. PMID: 17296977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Engle EC, Leigh RJ. Genes, brainstem developmental, and eye movements. Neurology 2002;59:304–05 - PubMed
-
- Pieh C, Lengyel D, Neff A, et al. Brainstem hypoplasia in familial horizontal gaze palsy and scoliosis. Neurology 2002;59:462–63 - PubMed
-
- Nuri Sener R. Congenital cleft in the pontomedullary junction: case report. J Comp Assist Tomogr 27:544–46 - PubMed
-
- Squirrel DM, Griffiths PD, Burke JP. Congenital cleavage of dorsal pons and medulla. J Pediatr Ophtalmol Strabismus 2001;38:308–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
