Histone modification-dependent and -independent pathways for recruitment of checkpoint protein Crb2 to double-strand breaks
- PMID: 16778077
- PMCID: PMC1482479
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1422606
Histone modification-dependent and -independent pathways for recruitment of checkpoint protein Crb2 to double-strand breaks
Abstract
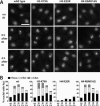
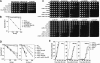
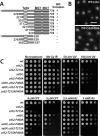
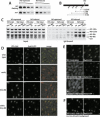
Cellular responses to DNA damage involve the relocalization of checkpoint proteins to DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs). The fission yeast checkpoint mediator protein Crb2, a homolog of mammalian 53BP1, forms ionizing radiation-induced nuclear foci (IRIF). The IRIF formation by Crb2 requires histone H2A C-terminal phosphorylation and H4-K20 methylation. However, the relevance of Crb2 relocalization is uncertain, because neither histone modification is required for a checkpoint response. Here we show that these histone modifications cooperate in the same Crb2 recruitment pathway, which also requires the Tudor and BRCT motifs in Crb2. In the absence of these histone modifications, an alternative recruitment pathway is sufficient for checkpoint activation and accumulation of Crb2 at a persistent DSB generated by HO endonuclease. This parallel pathway requires a cyclin-dependent kinase phosphorylation site in Crb2 that mediates an association with another BRCT protein Cut5 (the TopBP1 homolog), which also accumulates at HO-induced DSBs. We propose that such dual recruitment mechanisms may be a common feature of DNA damage checkpoint mediators.
Figures

References
-
- Canman C.E. Checkpoint mediators: Relaying signals from DNA strand breaks. Curr. Biol. 2003;13:R488–R490. - PubMed
-
- Capasso H., Palermo C., Wan S., Rao H., John U.P., O’Connell M.J., Walworth N.C. Phosphorylation activates Chk1 and is required for checkpoint-mediated cell cycle arrest. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:4555–4564. - PubMed
-
- Celeste A., Fernandez-Capetillo O., Kruhlak M.J., Pilch D.R., Staudt D.W., Lee A., Bonner R.F., Bonner W.M., Nussenzweig A. Histone H2AX phosphorylation is dispensable for the initial recognition of DNA breaks. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003;5:675–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
