Six-minute-walk distance predicts waiting list survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 16778159
- PMCID: PMC2648057
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200604-520OC
Six-minute-walk distance predicts waiting list survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
Rationale: Functional studies may be useful to predict survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Various cutoffs of 6-min-walk distance (6MWD) have been suggested to identify patients at a high risk of death.
Objectives: To examine the association between 6MWD and survival in patients with IPF listed for lung transplantation, and to identify sensitive and specific cutoffs for predicting death at 6 mo.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of 454 patients classified as having IPF listed for lung transplantation with the United Network for Organ Sharing between June 30, 2004 and July 22, 2005.
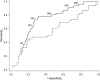
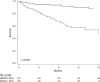
Measurements and main results: Lower 6MWD was associated with an increased mortality rate (p value for linear trend < 0.0001). Patients with a walk distance less than 207 m had a more than fourfold greater mortality rate than those with a walk distance of 207 m or more, despite adjustment for demographics, anthropomorphics, FVC % predicted, pulmonary hypertension, and medical comorbidities (adjusted rate ratio, 4.7; 95% confidence interval, 2.5-8.9; p < 0.0001). 6MWD was a significantly better predictor of 6-mo mortality than was FVC % predicted (c-statistic = 0.73 vs. 0.59, respectively; p = 0.02).
Conclusions: Lower 6MWD was strongly and independently associated with an increased mortality rate for wait-listed patients classified as having IPF. 6MWD was a better predictor of death at 6 mo than was FVC % predicted.
Figures
References
-
- Schwartz DA, Helmers RA, Galvin JR, Van Fossen DS, Frees KL, Dayton CS, Burmeister LF, Hunninghake GW. Determinants of survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;149:450–454. - PubMed
-
- King TE, Tooze JA, Schwarz MI, Brown KR, Cherniack RM. Predicting survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: scoring system and survival model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;164:1171–1181. - PubMed
-
- Martinez FJ, Keane MP. Update in diffuse parenchymal lung diseases 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2006;173:1066–1071. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;161:646–664. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

