Using Bayesian networks to predict survival of liver transplant patients
- PMID: 16779059
- PMCID: PMC1560677
Using Bayesian networks to predict survival of liver transplant patients
Abstract
The relative scarcity of grafts available for liver transplantation highlights the need to identify patients likely to have good outcomes after treatment. We used transplant information from the United Network for Organ Sharing database to construct a Bayesian network model to predict 90-day graft survival. The final model incorporated a set of 29 pre-transplant variables, and it achieved performance, as measured by area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, of 0.674 by cross-validation and 0.681 on an independent validation set. The results showed a positive predictive value of 91%, while the negative predictive value was lower at 30%. With additional refinement and validation, our model may be useful as an adjunct to clinical experience in identifying patients most likely to have good outcomes following liver transplantation.
Figures
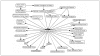

References
-
- 2003 OPTN/SRTR Annual Report: Transplant Data 1993 – 2002. HHS/HRSA/SPB/DOT; UNOS; URREA. (Chapter VII). www.ustransplant.org
-
- Gilbert JR, Pascual M, Schoenfeld DA, Rubin RH, Delmonico FL, Cosimi AB. Evolving trends in liver transplantation: an outcome and charge analysis. Transplantation. 1999;67(2):246–53. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network—HRSA. Final rule with comment period. Fed Regist. 1998;63:16296–338. - PubMed
-
- Thuluvath PJ, Yoo HY, Thompson RE. A model to predict survival at one month, one year, and five years after liver transplantation based on pretransplant clinical characteristics. Liver Transpl. 2003;9(5):527–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
