A dose-ranging study of AAV-hAADC therapy in Parkinsonian monkeys
- PMID: 16781894
- PMCID: PMC2725179
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2006.04.008
A dose-ranging study of AAV-hAADC therapy in Parkinsonian monkeys
Abstract
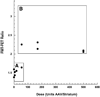
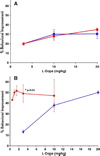
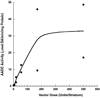
The main medication for idiopathic Parkinson disease is L-Dopa. Drug efficacy declines steadily in part because the converting enzyme, aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase (AADC), is lost concomitant with substantia nigra atrophy. Over the past decade, we have developed a gene therapy approach in which AADC activity is restored to the brain by infusion into the striatum of a recombinant adeno-associated virus carrying human AADC cDNA. We report here the results of an investigation of the relationship between vector dose and a series of efficacy markers, such as PET, L-Dopa response, and AADC enzymatic activity. At low doses of vector, no effect of vector was seen on PET or behavioral response. At higher doses, a sharp improvement in both parameters was observed, resulting in an approximate 50% improvement in L-Dopa responsiveness. The relationship between vector dose and AADC enzymatic activity in tissue extracts was linear. We conclude that little behavioral improvement can be seen until AADC activity reaches a level that is no longer rate limiting for conversion of clinical doses of L-Dopa into dopamine or for trapping of the PET tracer FMT. These findings have implications for the design and interpretation of clinical studies of AAV-hAADC gene therapy.
Figures

References
-
- Agid Y, Javoy F, Glowinski J. Hyperactivity of remaining dopaminergic neurons after partial destruction of the nigro-striatal dopaminergic system in the rat. Nat. New Biol. 1973;245:150–151. - PubMed
-
- Aminoff MJ. Parkinson’s disease. Neurol. Clin. 2001;19:119–128. vi. - PubMed
-
- Bankiewicz KS, et al. Convection-enhanced delivery of AAV vector in parkinsonian monkeys: in vivo detection of gene expression and restoration of dopaminergic function using pro-drug approach. Exp. Neurol. 2000;164:2–14. - PubMed
-
- Berheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewics O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F. Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington—Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J. Neurol. Sci. 1973;20:415–455. - PubMed
-
- Eberling JL, et al. PET [18F]6-fluoro-l-m-tyrosine imaging of MPTP-lesioned primates. Brain Res. 1997;750:264–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

