Murine isolated lymphoid follicles contain follicular B lymphocytes with a mucosal phenotype
- PMID: 16782693
- PMCID: PMC1570099
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpgi.00525.2005
Murine isolated lymphoid follicles contain follicular B lymphocytes with a mucosal phenotype
Abstract
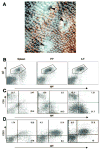
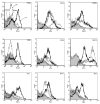
Isolated lymphoid follicles (ILFs) are organized intestinal lymphoid structures whose formation can be induced by luminal stimuli. ILFs have been demonstrated to act as inductive sites for the generation of immune responses directed toward luminal stimuli; however, the phenotype of the immune response initiated within ILFs has largely been uninvestigated. To gain a better understanding of the immune responses initiated within ILFs, we examined phenotypic and functional aspects of the largest cellular component of the murine ILF lymphocyte population, B lymphocytes. We observed that murine ILF B lymphocytes are composed of a relatively homogenous population of follicular B-2 B lymphocytes. Consistent with their proximity to multiple stimuli, ILF B lymphocytes displayed a more activated phenotype compared with their counterparts in the spleen and Peyer's patch (PP). ILF B lymphocytes also expressed higher levels of immunomodulatory B7 and CD28 family members B7X and programmed death-1 compared with their counterparts in the spleen and PP. ILF B lymphocytes preferentially differentiate into IgA-producing plasma cells and produce more IL-4 and IL-10 and less interferon-gamma compared with their counterparts in the spleen. Immunoglobulin repertoire analysis from individual ILFs demonstrated that ILFs contain a polyclonal population of B lymphocytes. These findings indicate that murine ILFs contain a polyclonal population of follicular B-2 B lymphocytes with a phenotype similar to PP B lymphocytes and that, in unchallenged animals, ILFs promote immune responses with a homeostatic phenotype.
Figures
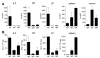
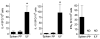
Similar articles
-
CC chemokine receptor 6 expression by B lymphocytes is essential for the development of isolated lymphoid follicles.Am J Pathol. 2007 Apr;170(4):1229-40. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060817. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17392163 Free PMC article.
-
Isolated lymphoid follicles can function as sites for induction of mucosal immune responses.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004 Dec;1029:44-57. doi: 10.1196/annals.1309.006. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004. PMID: 15681742
-
Adaptive immune responses are dispensable for isolated lymphoid follicle formation: antigen-naive, lymphotoxin-sufficient B lymphocytes drive the formation of mature isolated lymphoid follicles.J Immunol. 2005 May 1;174(9):5720-8. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.9.5720. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15843574
-
CCR6 and CCL20: partners in intestinal immunity and lymphorganogenesis.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006 Aug;1072:52-61. doi: 10.1196/annals.1326.036. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006. PMID: 17057190 Review.
-
Organizer and regulatory role of colonic isolated lymphoid follicles in inflammation.Acta Physiol Hung. 2012 Sep;99(3):344-52. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.99.2012.3.11. Acta Physiol Hung. 2012. PMID: 22982722 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of aging on urinary tract epithelial homeostasis and immunity.Dev Biol. 2023 Jan;493:29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2022.11.003. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36368522 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging impacts isolated lymphoid follicle development and function.Immun Ageing. 2011 Jan 7;8(1):1. doi: 10.1186/1742-4933-8-1. Immun Ageing. 2011. PMID: 21214915 Free PMC article.
-
A missense variant in SLC39A8 confers risk for Crohn's disease by disrupting manganese homeostasis and intestinal barrier integrity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Nov 17;117(46):28930-28938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2014742117. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33139556 Free PMC article.
-
CC chemokine receptor 6 expression by B lymphocytes is essential for the development of isolated lymphoid follicles.Am J Pathol. 2007 Apr;170(4):1229-40. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060817. Am J Pathol. 2007. PMID: 17392163 Free PMC article.
-
Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Supports Gut Mucosal Immunity and Commensal Microbiome Recognition in Autoimmune Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 29;13:748284. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.748284. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35422819 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agata Y, Kawasaki A, Nishimura H, Ishida Y, Tsubata T, Yagita H, Honjo T. Expression of the PD-1 antigen on the surface of stimulated mouse T and B lymphocytes. Int Immunol. 1996;8:765–772. - PubMed
-
- Berland R, Wortis HH. Origins and functions of B-1 cells with notes on the role of CD5. Annu Rev Immunol. 2002;20:253–300. - PubMed
-
- Budd RC, Cerottini JC, Horvath C, Bron C, Pedrazzini T, Howe RC, MacDonald HR. Distinction of virgin and memory T lymphocytes. Stable acquisition of the Pgp-1 glycoprotein concomitant with antigenic stimulation. J Immunol. 1987;138:3120–3129. - PubMed
-
- Cerwenka A, Carter LL, Reome JB, Swain SL, Dutton RW. In vivo persistence of CD8 polarized T cell subsets producing type 1 or type 2 cytokines. J Immunol. 1998;161:97–105. - PubMed
-
- Conrad DH, Waldschmidt TJ, Lee WT, Rao M, Keegan AD, Noelle RJ, Lynch RG, Kehry MR. Effect of B cell stimulatory factor-1 (interleukin 4) on Fc epsilon and Fc gamma receptor expression on murine B lymphocytes and B cell lines. J Immunol. 1987;139:2290–2296. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

