Immunohistochemical characterization of elastic system fibers in rat molar periodontal ligament
- PMID: 16782850
- PMCID: PMC3957806
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.5A6905.2006
Immunohistochemical characterization of elastic system fibers in rat molar periodontal ligament
Abstract
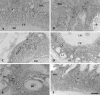
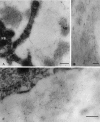
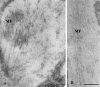
Among elastic system fibers, oxytalan fibers are known as a ubiquitous component of the periodontal ligament, but the localization and role of elastin-containing fibers, i.e., elastic and elaunin fibers, has yet to be clarified. In this study, we immunohistochemically investigated the localization of elastin and fibrillin, major proteins of elastin-containing fibers in the periodontal ligament of rat lower first molars. At the light microscope level, distribution of elastin-positive fibers was not uniform but often concentrated in the vicinity of blood vessels in the apical region of the ligament. In contrast, fibrillin-positive fibers were more widely distributed throughout the ligament, and the pattern of their distribution was comparable to the reported distribution of oxytalan fibers. At the ultrastructural level, assemblies or bundles of abundant fibrillin-containing microfibrils were intermingled with a small amount of elastin. This observation indicated that elastin-positive fibers observed under the light microscope were elaunin fibers. No mature elastic fibers, however, were found in the ligament. These results show that the major components of elastic system fibers in the periodontal ligament of the rat mandibular first molar were oxytalan and elaunin fibers, suggesting that the elastic system fibers play a role in the mechanical protection of the vascular system.
Figures


References
-
- Beertsen W, Everts V, van den Hooff A. (1974) Fine structure of fibroblasts in the periodontal ligament of the rat incisor and their possible role in tooth eruption. Arch Oral Biol 19:1087–1098 - PubMed
-
- Chantawiboonchai P, Warita H, Ohya K, Soma K. (1998) Confocal laser scanning-microscopic observations on the three-dimensional distribution of oxytalan fibres in mouse periodontal ligament. Arch Oral Biol 43:811–817 - PubMed
-
- Chavrier C. (1990) The elastic system fibres in healthy human gingiva. Arch Oral Biol 35:223–225s - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

