Mechanisms directing the nuclear localization of the CtBP family proteins
- PMID: 16782877
- PMCID: PMC1489157
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.02402-05
Mechanisms directing the nuclear localization of the CtBP family proteins
Abstract
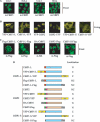
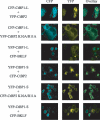
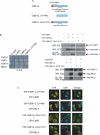
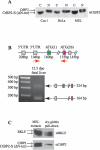
The C-terminal binding protein (CtBP) family includes four proteins (CtBP1 [CtBP1-L], CtBP3/BARS [CtBP1-S], CtBP2, and RIBEYE) which are implicated both in transcriptional repression and in intracellular trafficking. However, the precise mechanisms by which different CtBP proteins are targeted to different subcellular regions remains unknown. Here, we report that the nuclear import of the various CtBP proteins and splice isoforms is differentially regulated. We show that CtBP2 contains a unique nuclear localization signal (NLS) located within its N-terminal region, which contributes to its nuclear accumulation. Using heterokaryon assays, we show that CtBP2 is capable of shuttling between the nucleus and cytoplasm of the cell. Moreover, CtBP2 can heterodimerize with CtBP1-L and CtBP1-S and direct them to the nucleus. This effect strongly depends on the CtBP2 NLS. PXDLS motif-containing transcription factors, such as BKLF, that bind CtBP proteins can also direct them to the nucleus. We also report the identification of a splice isoform of CtBP2, CtBP2-S, that lacks the N-terminal NLS and localizes to the cytoplasm. Finally, we show that mutation of the CtBP NADH binding site impairs the ability of the proteins to dimerize and to associate with BKLF. This reduces the nuclear accumulation of CtBP1. Our results suggest a model in which the nuclear localization of CtBP proteins is influenced by the CtBP2 NLS, by binding to PXDLS motif partner proteins, and through the effect of NADH on CtBP dimerization.
Figures



References
-
- Balasubramanian, P., L. J. Zhao, and G. Chinnadurai. 2003. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide stimulates oligomerization, interaction with adenovirus E1A and an intrinsic dehydrogenase activity of CtBP. FEBS Lett. 537:157-160. - PubMed
-
- Barnes, C. J., R. K. Vadlamudi, S. K. Mishra, R. H. Jacobson, F. Li, and R. Kumar. 2003. Functional inactivation of a transcriptional corepressor by a signaling kinase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 10:622-628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
