Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase gamma is a marker for pyramidal cells and sensory neurons in the nervous system and is not necessary for normal development
- PMID: 16782895
- PMCID: PMC1489161
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00101-06
Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase gamma is a marker for pyramidal cells and sensory neurons in the nervous system and is not necessary for normal development
Abstract
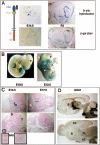
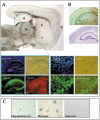
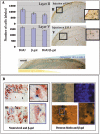
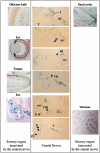
In order to gain insight into the biological role of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase gamma (RPTPgamma), we have generated RPTPgamma-null mice. RPTPgamma was disrupted by insertion of the beta-galactosidase gene under the control of the RPTPgamma promoter. As the RPTPgamma-null mice did not exhibit any obvious phenotype, we made use of these mice to study RPTPgamma expression and thus shed light on potential biological functions of this phosphatase. Inspection of mouse embryos shows that RPTPgamma is expressed in a variety of tissues during embryogenesis. RPTPgamma is expressed in both embryonic and adult brains. Specifically, we detected RPTPgamma expression in cortical layers II and V and in the stratum pyramidale of the hippocampus, indicating that RPTPgamma is a marker for pyramidal neurons. Mixed primary culture of glial cells showed a lack of expression of RPTPgamma in astrocytes and a low expression of RPTPgamma in oligodendrocytes and in microglia. Interestingly, RPTPgamma expression was detected in all sensory organs, including the ear, nose, tongue, eye, and vibrissa follicles, suggesting a potential role of RPTPgamma in sensory neurons. An initial behavioral analysis showed minor changes in the RPTPgamma-null mice.
Figures



References
-
- Barnea, G., O. Silvennoinen, B. Shaanan, A. M. Honegger, P. D. Canoll, P. D'Eustachio, B. Morse, J. B. Levy, S. Laforgia, K. Huebner, J. M. Musacchio, J. Sap, and J. Schlessinger. 1993. Identification of a carbonic anhydrase-like domain in the extracellular region of RPTPγ defines a new subfamily of receptor tyrosine phosphatases. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13:1497-1506. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bixby, J. L. 2001. Ligands and signaling through receptor-type tyrosine phosphatases. IUBMB Life 51:157-163. - PubMed
-
- Canoll, P. D., G. Barnea, J. B. Levy, J. Sap, M. Ehrlich, O. Silvennoinen, J. Schlessinger, and J. M. Musacchio. 1993. The expression of a novel receptor-type tyrosine phosphatase suggests a role in morphogenesis and plasticity of the nervous system. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 75:293-298. - PubMed
-
- Chilton, J. K., and A. W. Stoker. 2000. Expression of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases in embryonic chick spinal cord. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 16:470-480. - PubMed
-
- Danscher, G., and J. Zimmer. 1978. An improved Timm sulphide silver method for light and electron microscopic localization of heavy metals in biological tissues. Histochemistry 55:27-40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
