Poor performance of bootstrap confidence intervals for the location of a quantitative trait locus
- PMID: 16783000
- PMCID: PMC1569776
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.061549
Poor performance of bootstrap confidence intervals for the location of a quantitative trait locus
Abstract
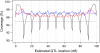
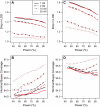
The aim of many genetic studies is to locate the genomic regions (called quantitative trait loci, QTL) that contribute to variation in a quantitative trait (such as body weight). Confidence intervals for the locations of QTL are particularly important for the design of further experiments to identify the gene or genes responsible for the effect. Likelihood support intervals are the most widely used method to obtain confidence intervals for QTL location, but the nonparametric bootstrap has also been recommended. Through extensive computer simulation, we show that bootstrap confidence intervals behave poorly and so should not be used in this context. The profile likelihood (or LOD curve) for QTL location has a tendency to peak at genetic markers, and so the distribution of the maximum-likelihood estimate (MLE) of QTL location has the unusual feature of point masses at genetic markers; this contributes to the poor behavior of the bootstrap. Likelihood support intervals and approximate Bayes credible intervals, on the other hand, are shown to behave appropriately.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Improved confidence intervals in quantitative trait loci mapping by permutation bootstrapping.Genetics. 2002 Apr;160(4):1673-86. doi: 10.1093/genetics/160.4.1673. Genetics. 2002. PMID: 11973320 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of the confidence interval of quantitative trait Loci location.Behav Genet. 2004 Jul;34(4):477-82. doi: 10.1023/B:BEGE.0000023652.93162.e8. Behav Genet. 2004. PMID: 15082944
-
Targeted Recombinant Progeny: a design for ultra-high resolution mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci in crosses between inbred or pure lines.BMC Genet. 2015 Jul 7;16:76. doi: 10.1186/s12863-015-0206-z. BMC Genet. 2015. PMID: 26148479 Free PMC article.
-
Empirical nonparametric bootstrap strategies in quantitative trait loci mapping: conditioning on the genetic model.Genetics. 1998 Jan;148(1):525-35. doi: 10.1093/genetics/148.1.525. Genetics. 1998. PMID: 9475761 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Bayesian multiple quantitative trait loci mapping in experimental crosses.Heredity (Edinb). 2008 Mar;100(3):240-52. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6801074. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Heredity (Edinb). 2008. PMID: 17987056 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Selecting subsets of genotyped experimental populations for phenotyping to maximize genetic diversity.Theor Appl Genet. 2013 Feb;126(2):379-88. doi: 10.1007/s00122-012-1986-4. Epub 2012 Oct 5. Theor Appl Genet. 2013. PMID: 23052022
-
Exercise and diet affect quantitative trait loci for body weight and composition traits in an advanced intercross population of mice.Physiol Genomics. 2012 Dec 1;44(23):1141-53. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00115.2012. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Physiol Genomics. 2012. PMID: 23048196 Free PMC article.
-
QTL mapping of natural variation reveals that the developmental regulator bruno reduces tolerance to P-element transposition in the Drosophila female germline.PLoS Biol. 2018 Oct 30;16(10):e2006040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006040. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 30376574 Free PMC article.
-
Modifiers of von Willebrand factor identified by natural variation in inbred strains of mice.Blood. 2009 Dec 17;114(26):5368-74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-07-233213. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19789385 Free PMC article.
-
Statistical dissection of cyto-nuclear epistasis subject to genomic imprinting in line crosses.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 18;9(3):e91702. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091702. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24643065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beran, R., 2003. The impact of the bootstrap on statistical algorithms and theory. Stat. Sci. 18: 175–184.
-
- Broman, K. W., H. Wu, Ś. Sen and G. A. Churchill, 2003. R/qtl: QTL mapping in experimental crosses. Bioinformatics 19: 889–890. - PubMed
-
- Dempster, A. P., N. M. Laird and D. B. Rubin, 1977. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 39: 1–38.
-
- Haley, C. S., and S. A. Knott, 1992. A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 69: 315–324. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

