Nucleotide variation and haplotype diversity in a 10-kb noncoding region in three continental human populations
- PMID: 16783003
- PMCID: PMC1569808
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.060301
Nucleotide variation and haplotype diversity in a 10-kb noncoding region in three continental human populations
Abstract
Noncoding regions are usually less subject to natural selection than coding regions and so may be more useful for studying human evolution. The recent surveys of worldwide DNA variation in four 10-kb noncoding regions revealed many interesting but also some incongruent patterns. Here we studied another 10-kb noncoding region, which is in 6p22. Sixty-six single-nucleotide polymorphisms were found among the 122 worldwide human sequences, resulting in 46 genotypes, from which 48 haplotypes were inferred. The distribution patterns of DNA variation, genotypes, and haplotypes suggest rapid population expansion in relatively recent times. The levels of polymorphism within human populations and divergence between humans and chimpanzees at this locus were generally similar to those for the other four noncoding regions. Fu and Li's tests rejected the neutrality assumption in the total sample and in the African sample but Tajima's test did not reject neutrality. A detailed examination of the contributions of various types of mutations to the parameters used in the neutrality tests clarified the discrepancy between these test results. The age estimates suggest a relatively young history in this region. Combining three autosomal noncoding regions, we estimated the long-term effective population size of humans to be 11,000 +/- 2800 using Tajima's estimator and 17,600 +/- 4700 using Watterson's estimator and the age of the most recent common ancestor to be 860,000 +/- 258,000 years ago.
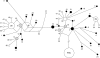
Figures
References
-
- Bandelt, H. J., P. Forster and A. Rohl, 1999. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 16: 37–48. - PubMed
-
- Cann, R. L., M. Stoneking and A. C. Wilson, 1987. Mitochondrial DNA and human evolution. Nature 325: 31–36. - PubMed
-
- Eswaran, V., H. Harpending and A. R. Rogers, 2005. Genomics refutes an exclusively African origin of humans. J. Hum. Evol. 49: 1–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

