The RAD6/BRE1 histone modification pathway in Saccharomyces confers radiation resistance through a RAD51-dependent process that is independent of RAD18
- PMID: 16783014
- PMCID: PMC1569736
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.057794
The RAD6/BRE1 histone modification pathway in Saccharomyces confers radiation resistance through a RAD51-dependent process that is independent of RAD18
Abstract
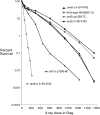
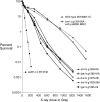
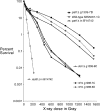
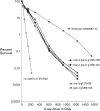
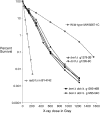
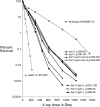
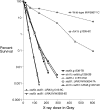
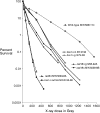
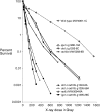
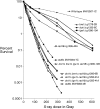
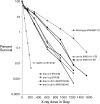
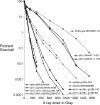
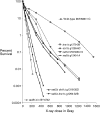
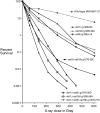
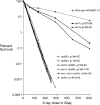
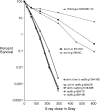
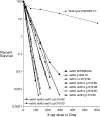
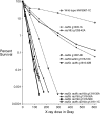
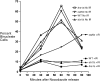
We examine ionizing radiation (IR) sensitivity and epistasis relationships of several Saccharomyces mutants affecting post-translational modifications of histones H2B and H3. Mutants bre1Delta, lge1Delta, and rtf1Delta, defective in histone H2B lysine 123 ubiquitination, show IR sensitivity equivalent to that of the dot1Delta mutant that we reported on earlier, consistent with published findings that Dot1p requires H2B K123 ubiquitination to fully methylate histone H3 K79. This implicates progressive K79 methylation rather than mono-methylation in IR resistance. The set2Delta mutant, defective in H3 K36 methylation, shows mild IR sensitivity whereas mutants that abolish H3 K4 methylation resemble wild type. The dot1Delta, bre1Delta, and lge1Delta mutants show epistasis for IR sensitivity. The paf1Delta mutant, also reportedly defective in H2B K123 ubiquitination, confers no sensitivity. The rad6Delta, rad51null, rad50Delta, and rad9Delta mutations are epistatic to bre1Delta and dot1Delta, but rad18Delta and rad5Delta show additivity with bre1Delta, dot1Delta, and each other. The bre1Delta rad18Delta double mutant resembles rad6Delta in sensitivity; thus the role of Rad6p in ubiquitinating H2B accounts for its extra sensitivity compared to rad18Delta. We conclude that IR resistance conferred by BRE1 and DOT1 is mediated through homologous recombinational repair, not postreplication repair, and confirm findings of a G1 checkpoint role for the RAD6/BRE1/DOT1 pathway.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Dot1-dependent histone H3 methylation in G1 and S phase DNA damage checkpoint functions of Rad9.Mol Cell Biol. 2005 Oct;25(19):8430-43. doi: 10.1128/MCB.25.19.8430-8443.2005. Mol Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 16166626 Free PMC article.
-
The role of RAD6 in recombinational repair, checkpoints and meiosis via histone modification.DNA Repair (Amst). 2009 Apr 5;8(4):470-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2009.01.007. Epub 2009 Feb 18. DNA Repair (Amst). 2009. PMID: 19230796 Review.
-
Rad6-Bre1-mediated histone H2B ubiquitylation modulates the formation of double-strand breaks during meiosis.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004 Aug 3;101(31):11380-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400078101. Epub 2004 Jul 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004. PMID: 15280549 Free PMC article.
-
Rad6-Bre1 mediated histone H2Bub1 protects uncapped telomeres from exonuclease Exo1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.DNA Repair (Amst). 2018 Dec;72:64-76. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 17. DNA Repair (Amst). 2018. PMID: 30254011
-
The Bre1/Rad6 machinery: writing the central histone ubiquitin mark on H2B and beyond.Chromosome Res. 2020 Dec;28(3-4):247-258. doi: 10.1007/s10577-020-09640-3. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Chromosome Res. 2020. PMID: 32895784 Review.
Cited by
-
A chromatin scaffold for DNA damage recognition: how histone methyltransferases prime nucleosomes for repair of ultraviolet light-induced lesions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Feb 28;48(4):1652-1668. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1229. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31930303 Free PMC article.
-
Essential roles of Rad6 in conidial property, stress tolerance, and pathogenicity of Beauveria bassiana.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2362748. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2362748. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 38860453 Free PMC article.
-
Bre1-dependent H2B ubiquitination promotes homologous recombination by stimulating histone eviction at DNA breaks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 30;46(21):11326-11339. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky918. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30304473 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad6 postreplication repair and Siz1/Srs2 homologous recombination-inhibiting pathways process DNA damage that arises in asf1 mutants.Mol Cell Biol. 2009 Oct;29(19):5226-37. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00894-09. Epub 2009 Jul 27. Mol Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19635810 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H3 K79 methylation states play distinct roles in UV-induced sister chromatid exchange and cell cycle checkpoint arrest in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jun;42(10):6286-99. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku242. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24748660 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brachmann, C. B., A. Davies, G. J. Cost, E. Caputo, J. Li et al., 1998. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast 14: 115–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

