Stimulation of sensory neuropeptide release by nociceptin/orphanin FQ leads to hyperaemia in acutely inflamed rat knees
- PMID: 16783411
- PMCID: PMC1751929
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706804
Stimulation of sensory neuropeptide release by nociceptin/orphanin FQ leads to hyperaemia in acutely inflamed rat knees
Abstract
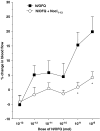
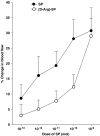
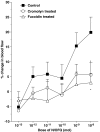
The peripheral effect of the 'opioid-like' peptide nociceptin/orphanin FQ (N/OFQ) on joint blood flow was investigated in acutely inflamed rats. Sensory neuropeptide release from capsaicin-sensitive nerves and the involvement of synovial mast cells and leukocytes on these vasomotor responses were also studied. Blood flow measurements of exposed knee joints were performed in urethane-anaesthetised rats (2 mg kg(-1) intraperitoneal) using laser Doppler perfusion imaging. Topical administration of N/OFQ (10(-13)-10(-8) mol) to acutely inflamed joints caused a dose-dependent increase in synovial perfusion with an ED(50) of 4.0 x 10(-10) mol. This vasodilatatory response was blocked by the selective NOP receptor antagonist [Phe(1)-(CH(2)-NH)-Gly(2)]-Nociceptin(1-13)-NH(2) (10(-9) mol) (P<0.0001).Co-administration of N/OFQ with the neurokinin-1 (NK(1)) receptor antagonist [D-Arg1,D-Phe5,D-Trp7,9,Leu11]-Substance P (10(-12) mol), the vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) receptor antagonist VIP(6-28) (10(-9) mol) or the calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist CGRP(8-37) (10(-9) mol) all blocked the hyperaemic effect of N/OFQ (P<0.0001). Treatment of acutely inflamed knees with capsaicin (8-methyl-N-vanillyl-6-noneamide) to destroy unmyelinated joint afferents also inhibited N/OFQ vasomotor activity. Stabilisation of synovial mast cells with disodium cromoglycate (cromolyn) ameliorated N/OFQ responses, whereas inactivation of circulating leukocytes with the pan-selectin inhibitor fucoidin completely blocked N/OFQ-induced hyperaemia in these joints. These experiments show that in acutely inflamed knee joints, N/OFQ acts on NOP receptors located on synovial mast cells and leukocytes leading to the secondary release of proinflammatory mediators into the joint. These agents subsequently stimulate sensory neuropeptide release from capsaicin-sensitive nerves culminating in vasodilatation and increased articular blood flow.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The role of joint nerves and mast cells in the alteration of vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) sensitivity during inflammation progression in rats.Br J Pharmacol. 2005 May;145(1):104-13. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706169. Br J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15723091 Free PMC article.
-
Nociceptin/orphanin FQ evokes knee joint pain in rats via a mast cell independent mechanism.Neurosci Lett. 2006 May 1;398(1-2):135-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2005.12.066. Epub 2006 Jan 19. Neurosci Lett. 2006. PMID: 16423460
-
Involvement of sympathetic efferents but not capsaicin-sensitive afferents in nociceptin-mediated dual control of rat synovial blood flow.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003 Jun;284(6):R1477-85. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00733.2002. Epub 2003 Feb 6. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12573980
-
The role of orphanin FQ/nociceptin in neuroplasticity: relationship to stress, anxiety and neuroinflammation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Oct 8;7:173. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00173. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24155687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reverse physiology: discovery of the novel neuropeptide, orphanin FQ/nociceptin.Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1998;12(3):163-76. doi: 10.1615/critrevneurobiol.v12.i3.10. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1998. PMID: 9847053 Review.
Cited by
-
TNF-Alpha as an Initiator of Allodynia and Anxiety-Like Behaviors in a Preclinical Model of PTSD and Comorbid Pain.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Aug 25;12:721999. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.721999. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34512420 Free PMC article.
-
The nociceptin/orphanin FQ receptor system as a target to alleviate cancer-induced bone pain in rats: Model validation and pharmacological evaluation.Br J Pharmacol. 2021 May;178(9):1995-2007. doi: 10.1111/bph.14899. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Br J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 31724155 Free PMC article.
-
ZP120 causes relaxation by pre-junctional inhibition of noradrenergic neurotransmission in rat mesenteric resistance arteries.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Mar;153(6):1185-94. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707688. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18193068 Free PMC article.
-
NOP Receptor Ligands as Potential Agents for Inflammatory and Autoimmune Diseases.J Amino Acids. 2011;2011:836569. doi: 10.4061/2011/836569. Epub 2011 Nov 17. J Amino Acids. 2011. PMID: 22312472 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo effects of CB2 receptor-selective cannabinoids on the vasculature of normal and arthritic rat knee joints.Br J Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;153(2):358-66. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707565. Epub 2007 Nov 5. Br J Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 17982474 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ACKERMANN P.W., SPETEA M., NYLANDER I., PLOJ K., AHMED M., KREICBERGS A. An opioid system in connective tissue. A study of achilles tendon in the rat. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001;49:1387–1396. - PubMed
-
- ANDOH T., ITOH M., KURAISHI Y. Nociceptin gene expression in rat dorsal root ganglia induced by peripheral inflammation. Neuroreport. 1997;8:2793–2796. - PubMed
-
- ARNDT M.L., WU D., SOONG Y., SZETO H.H. Nociceptin/orphanin FQ increases blood pressure and heart rate via sympathetic activation in sheep. Peptides. 1999;20:465–470. - PubMed
-
- BIGONI R., GIULIANI S., CALO G., RIZZI A., GUERRINI R., SALVADORI S., REGOLI D., MAGGI C.A. Characterization of nociceptin receptors in the periphery: in vitro and in vivo studies. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol. 1999;359:160–167. - PubMed
-
- CARPENTER K.J., VITHLANI M., DICKENSON A.H. Unaltered peripheral excitatory actions of nociceptin contrast with enhanced spinal inhibitory effects after carrageenan inflammation: an electrophysiological study in the rat. Pain. 2000;85:433–441. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

