Linking DNA-binding proteins to their recognition sequences by using protein microarrays
- PMID: 16785442
- PMCID: PMC1502558
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0509185103
Linking DNA-binding proteins to their recognition sequences by using protein microarrays
Abstract
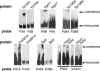
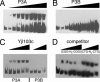
Analyses of whole-genome sequences and experimental data sets have revealed a large number of DNA sequence motifs that are conserved in many species and may be functional. However, methods of sufficient scale to explore the roles of these elements are lacking. We describe the use of protein arrays to identify proteins that bind to DNA sequences of interest. A microarray of 282 known and potential yeast transcription factors was produced and probed with oligonucleotides of evolutionarily conserved sequences that are potentially functional. Transcription factors that bound to specific DNA sequences were identified. One previously uncharacterized DNA-binding protein, Yjl103, was characterized in detail. We defined the binding site for this protein and identified a number of its target genes, many of which are involved in stress response and oxidative phosphorylation. Protein microarrays offer a high-throughput method for determining DNA-protein interactions.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: M.S. consults for Invitrogen.
Figures



References
-
- Cliften P., Sudarsanam P., Desikan A., Fulton L., Fulton B., Majors J., Waterston R., Cohen B. A., Johnston M. Science. 2003;301:71–76. - PubMed
-
- Kellis M., Patterson N., Endrizzi M., Birren B., Lander E. S. Nature. 2003;423:241–254. - PubMed
-
- Venkatesh B., Yap W. H. BioEssays. 2005;27:100–107. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

