Has Cox-2 a prognostic role in non-small-cell lung cancer? A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis of the survival results
- PMID: 16786043
- PMCID: PMC2360613
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603226
Has Cox-2 a prognostic role in non-small-cell lung cancer? A systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis of the survival results
Abstract
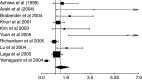
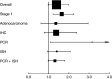
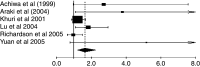
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) is overexpressed in lung cancer, especially in adenocarcinoma (ADC). Our aim was to determine the prognostic value of COX-2 on survival in patients with lung cancer. Studies evaluating the survival impact of COX-2 in lung cancer, published until December 2005, were selected. Data for estimation of individual hazard ratios (HR) for survival were extracted from the publications and combined in a pooled HR. Among 14 eligible papers, all dealing with non-small-cell lung cancer, 10 provided results for meta-analysis of survival data (evaluable studies). Cyclooxygenase-2 positivity was associated with reduced survival, improved survival or no statistically significant impact in six, one and seven studies, respectively. Combined HR for the 10 evaluable studies (1236 patients) was 1.39 (95% confidence intervals (CI): 0.97-1.99). In stage I lung cancer (six evaluable studies, 554 patients), it was 1.64 (95% CI: 1.21-2.24). No significant impact was shown in ADC. A slight detrimental effect on survival in patients with lung cancer is associated with COX-2 expression, but the statistical significance is not reached. This effect is statistically significant in stage I, suggesting that COX-2 expression could be useful at early stages to distinguish those with a worse prognosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cox-2 in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2013 Apr 18;419:26-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2013.01.012. Epub 2013 Feb 4. Clin Chim Acta. 2013. PMID: 23384501
-
Expression of p16 in non-small cell lung cancer and its prognostic significance: a meta-analysis of published literatures.Lung Cancer. 2011 Nov;74(2):155-63. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2011.04.019. Epub 2011 May 31. Lung Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21621871
-
A meta-analysis of STAT3 and phospho-STAT3 expression and survival of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014 Mar;40(3):311-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2013.11.012. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24332948 Review.
-
Eicosanoid modulation in advanced lung cancer: cyclooxygenase-2 expression is a positive predictive factor for celecoxib + chemotherapy--Cancer and Leukemia Group B Trial 30203.J Clin Oncol. 2008 Feb 20;26(6):848-55. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.13.8081. J Clin Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18281656 Clinical Trial.
-
The clinicopathologic impacts and prognostic significance of GLUT1 expression in patients with lung cancer: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2019 Mar 20;689:76-83. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2018.12.006. Epub 2018 Dec 12. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30552981 Review.
Cited by
-
Prognostic factors in resected lung carcinomas.EJC Suppl. 2013 Sep;11(2):137-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcsup.2013.07.023. EJC Suppl. 2013. PMID: 26217123 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Effects of COX-2 inhibition on expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-8 in lung cancer cells.BMC Cancer. 2008 Jul 31;8:218. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-218. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18671849 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of cyclooxygenase-2 over-expression on the prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. An experience from Western Saudi Arabia.Saudi Med J. 2018 Aug;39(8):773-780. doi: 10.15537/smj.2018.8.22837. Saudi Med J. 2018. PMID: 30106414 Free PMC article.
-
Blood vessel invasion as a strong independent prognostic indicator in non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28844. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028844. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22194927 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of COX-2 immunohistochemical expression in colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis of the literature.PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e58891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058891. Epub 2013 Mar 20. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23527044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ab' Saber AM, Massoni Neto LM, Bianchi CP, Ctenas BB, Parra ER, Eher EM, Pereira JC, Takagaki T, Yamaguchi NH, Capelozzi VL (2004) Neuroendocrine and biologic features of primary tumors and tissue in pulmonary large cell carcinomas. Ann Thorac Surg 77: 1883–1890 - PubMed
-
- Achiwa H, Yatabe Y, Hida T, Kuroishi T, Kozaki K, Nakamura S, Ogawa M, Sugiura T, Mitsudomi T, Takahashi T (1999) Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase 2 expression in primary, resected lung adenocarcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 5: 1001–1005 - PubMed
-
- Altorki NK, Port JL, Zhang F, Golijanin D, Thaler HT, Duffield-Lillico AJ, Subbaramaiah K, Dannenberg AJ (2005) Chemotherapy induces the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11: 4191–4197 - PubMed
-
- Araki K, Hashimoto K, Ardyanto TD, Osaki M, Shomori K, Nakamura H, Ito H (2004) Co-expression of Cox-2 and EGFR in stage I human bronchial adenocarcinomas. Lung Cancer 45: 161–169 - PubMed
-
- Boyle P, Ferlay J (2005) Cancer incidence and mortality in Europe, 2004. Ann Oncol 16: 481–488 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

