Regulation of GLUT4 gene expression by SREBP-1c in adipocytes
- PMID: 16787385
- PMCID: PMC1570175
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20060696
Regulation of GLUT4 gene expression by SREBP-1c in adipocytes
Abstract
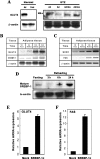
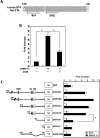
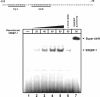
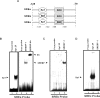
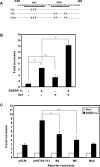
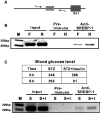
Expression of the GLUT4 (glucose transporter type 4 isoform) gene in adipocytes is subject to hormonal or metabolic control. In the present study, we have characterized an adipose tissue transcription factor that is influenced by fasting/refeeding regimens and insulin. Northern blotting showed that refeeding increased GLUT4 mRNA levels for 24 h in adipose tissue. Consistent with an increased GLUT4 gene expression, the mRNA levels of SREBP (sterol-regulatory-element-binding protein)-1c in adipose tissue were also increased by refeeding. In streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats, insulin treatment increased the mRNA levels of GLUT4 in adipose tissue. Serial deletion, luciferase reporter assays and electrophoretic mobility-shift assay studies indicated that the putative sterol response element is located in the region between bases -109 and -100 of the human GLUT4 promoter. Transduction of the SREBP-1c dominant negative form to differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes caused a reduction in the mRNA levels of GLUT4, suggesting that SREBP-1c mediates the transcription of GLUT4. In vivo chromatin immunoprecipitation revealed that refeeding increased the binding of SREBP-1 to the putative sterol-response element in the GLUT4. Furthermore, treating streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats with insulin restored SREBP-1 binding. In addition, we have identified an Sp1 binding site adjacent to the functional sterol-response element in the GLUT4 promoter. The Sp1 site appears to play an additive role in SREBP-1c mediated GLUT4 gene upregulation. These results suggest that upregulation of GLUT4 gene transcription might be directly mediated by SREBP-1c in adipose tissue.
Figures

References
-
- Shepherd P. R., Kahn B. B. Glucose transporters and insulin action: implications for insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999;341:248–257. - PubMed
-
- Furtado L. M., Somwar R., Sweeney G., Niu W., Klip A. Activation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 by insulin. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002;80:569–578. - PubMed
-
- Porte D., Jr Banting lecture 1990. Beta-cells in type II diabetes mellitus. Diabetes. 1991;40:166–180. - PubMed
-
- Kahn C. R. Banting lecture 1994. Insulin action, diabetogenes and the cause of type II diabetes. Diabetes. 1994;43:1066–1084. - PubMed
-
- Reaven G. M. Pathophysiology of insulin resistance in human disease. Physiol. Rev. 1995;75:473–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

