Tissue-specific expression of TRP channel genes in the mouse and its variation in three different mouse strains
- PMID: 16787531
- PMCID: PMC1557673
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-7-159
Tissue-specific expression of TRP channel genes in the mouse and its variation in three different mouse strains
Abstract
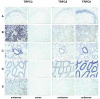
Background: The purpose of this work was to study the gene expression of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels in the mouse. The application of a standardized and quantitative technique, TaqMan RT-PCR, should give information about the pattern and relative importance of TRP channels for murine tissues and cell types. To verify data sets with an independent method, we studied the occurrence of some of the transcripts by in situ hybridization.
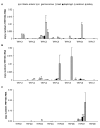
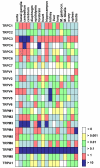
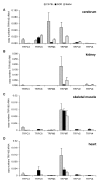
Results: We have characterized the mRNA expression of 22 TRP channels in the mouse with a focus on nerve and muscle tissues. This is the first study to describe the expression profiles of all channel isoforms of the four related Group 1 subfamilies (TRPC, TRPV, TRPM and TRPA) with a standardized and quantitative technique. Comparisons of transcript abundance showed a consistent dominance of TRPM7 and TRPC3 in most tissues. We further observed characteristic patterns and differences in gene expression of individual channels ranging over three orders of magnitude. The overall level of TRP channel mRNAs was highest in brain areas followed by kidney, lung, reproductive organs and muscle. In brain TRPM3 and TRPM7 dominated and 19 other isoforms were detected. In lung and kidney TRPV4, TRPV5 and TRPM7 were found in highest levels. TRPM7, TRPC3, TRPC6 and TRPM3 mRNAs were characteristically present in all tested muscle tissues. Most data obtained with the C57Bl/10 mouse strain were confirmed with Balb/c and NOD mice. However, TRPC3, C6, TRPM7, M3, TRPV2 and V4 expression showed marked differences in the three tested mouse strains. In situ hybridization revealed co-expression of transcripts on the cellular level and widely confirmed the data obtained with RT-PCR.
Conclusion: Transcripts coding for members of the TRPC, TRPV, TRPM and TRPA subfamilies of TRP cation channels are present in a broad spectrum of murine tissues. Several channel isoforms often coexist in a specific tissue or cell type. TRP channel expression does not show typical tissue specific dominance of individual members as is known from other ion channel families. Mouse strain specific variations of TRP channel expression indicate that genetic background or physiological requirements considerably influence expression levels.
Figures

References
-
- Montell C, Birnbaumer L, Flockerzi V, Bindels RJ, Bruford EA, Caterina MJ, Clapham DE, Harteneck C, Heller S, Julius D, Kojima I, Mori Y, Penner R, Prawitt D, Scharenberg AM, Schultz G, Shimizu N, Zhu MX. A unified nomenclature for the superfamily of TRP cation channels. Mol Cell. 2002;9:229–231. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(02)00448-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

