Effects of equipment and technique on peak flow measurements
- PMID: 16787543
- PMCID: PMC1525195
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2466-6-14
Effects of equipment and technique on peak flow measurements
Abstract
Background: Different lung function equipment and different respiratory manoeuvres may produce different Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF) results. Although the PEF is the most common lung function test, there have been few studies of these effects and no previous study has evaluated both factors in a single group of patients.
Methods: We studied 36 subjects (PEF range 80-570 l/min). All patients recorded PEF measurements using a short rapid expiration following maximal inspiration (PEF technique) or a forced maximal expiration to residual volume (FVC technique). Measurements were made using a Wright's peak flow meter, a turbine spirometer and a Fleisch pneumotachograph spirometer.
Results: The mean PEF was 8.7% higher when the PEF technique was used (compared with FVC technique, p < 0.0001). The mean PEF recorded with the turbine spirometer was 5.5% lower than the Wright meter reading. The Fleisch spirometer result was 19.5% lower than the Wright reading. However, adjustment of the Wrights measurements from the traditional Wright's scale to the new EU Peak Flow scale produced results that were only 7.2% higher than the Fleisch pneumotachograph measurements.
Conclusion: Peak flow measurements are affected by the instruction given and by the device and Peak Flow scale used. Patient management decisions should not be based on PEF measurement made on different instruments.
Figures

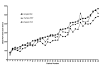

Similar articles
-
Evaluation of a new electronic spirometer: the vitalograph "Escort" spirometer.Thorax. 1994 Feb;49(2):175-8. doi: 10.1136/thx.49.2.175. Thorax. 1994. PMID: 8128409 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the turbine pocket spirometer.Thorax. 1987 Sep;42(9):689-93. doi: 10.1136/thx.42.9.689. Thorax. 1987. PMID: 3686460 Free PMC article.
-
Lung function measurement in general practice: a comparison of the Escort spirometer with the Micromed turbine spirometer and the mini-Wright peak flow meter.Respir Med. 1995 Nov;89(10):657-63. doi: 10.1016/0954-6111(95)90132-9. Respir Med. 1995. PMID: 8570879 Clinical Trial.
-
Incorrect use of peak flow meters: are you observing your patients?J Asthma. 2014 Aug;51(6):566-72. doi: 10.3109/02770903.2014.914218. Epub 2014 May 9. J Asthma. 2014. PMID: 24720711 Review.
-
[Comparison of different types of peak flow meter and reference values for peak expiratory flow (PEF) for healthy Japanese subjects].Nihon Rinsho. 1996 Nov;54(11):2927-32. Nihon Rinsho. 1996. PMID: 8950932 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A review on the transmission of COVID-19 based on cough/sneeze/breath flows.Eur Phys J Plus. 2022;137(1):1. doi: 10.1140/epjp/s13360-021-02162-9. Epub 2021 Dec 10. Eur Phys J Plus. 2022. PMID: 34909366 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relation of Changes in PEF and FEV1 During Salbutamol-Induced Bronchodilation After Methacholine Challenge Test.Pulm Med. 2025 Jul 7;2025:7675935. doi: 10.1155/pm/7675935. eCollection 2025. Pulm Med. 2025. PMID: 40661699 Free PMC article.
-
Joint Indian Chest Society-National College of Chest Physicians (India) guidelines for spirometry.Lung India. 2019 Apr;36(Supplement):S1-S35. doi: 10.4103/lungindia.lungindia_300_18. Lung India. 2019. PMID: 31006703 Free PMC article.
-
Lower peak expiratory flow rate is associated with a higher risk of pneumonia in patients with stroke.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2024 Dec;60(6):929-937. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.24.08475-2. Epub 2024 Oct 23. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2024. PMID: 39441112 Free PMC article.
-
Guidelines for diagnosis and management of bronchial asthma: Joint ICS/NCCP (I) recommendations.Lung India. 2015 Apr;32(Suppl 1):S3-S42. doi: 10.4103/0970-2113.154517. Lung India. 2015. PMID: 25948889 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Shaw A, Fisher J. Calibration of some instruments for measuring peak expiratory flow. J Med Eng Technol. 1980;4:291–4. - PubMed
-
- Miller M. Peak expiratory flow meter scale changes: implications for patients and health professionals. Airways J. 2004;2:80–82.
-
- Quanjer PH, Tammeling GJ, Cotes JE, Pedersen OF, Peslin R, Yernault JC. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Eur Respir J. 1993;6:5–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

