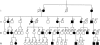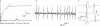Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A duplication with severe paresis of the proximal lower limb muscles: a long-term follow-up study
- PMID: 16788010
- PMCID: PMC2077541
- DOI: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.093443
Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A duplication with severe paresis of the proximal lower limb muscles: a long-term follow-up study
Abstract
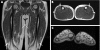
Objective: To describe a large pedigree with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1A (CMT1A) duplication in which severe pelvic and thigh musculature weakness occurred in two patients, detected by analysing the leg muscle atrophy pattern on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods: The pedigree comprised 18 patients, aged between 15 and 85 (median 46) years, who were serially evaluated for up to three decades. All 18 patients and 13 non-affected at-risk people underwent electrophysiological examination. An MRI study of lower limb musculature was carried out in four patients. Three patients underwent sural-nerve biopsy. Genetic testing was carried out in 17 patients and in all 13 at-risk normal people.
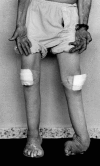
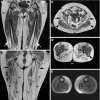
Results: Fourteen patients were asymptomatic or slightly disabled. The two oldest patients, aged 84 and 80, showed a moderate phenotype. Two other patients, aged 70 and 53, showed late-onset and gradually progressive peroneal paresis extending up to the thigh and pelvic musculature, resulting in waddling gait. MRI scans of all three patients with a mild phenotype showed subtle and subclinical fatty infiltration of calf anterolateral muscle compartments, with thigh muscle involvement in one patient, and extensive atrophy of intrinsic foot muscles. In the youngest patient with proximal leg weakness, the MRI scan showed massive fatty atrophy of all the calf muscles, posteromedial thigh muscle compartments, and internal and external hip rotator muscles. Sural-nerve biopsy specimens showed hypertrophic neuropathy with no superimposed inflammation. Good correlation was seen between electrophysiological and genetic testing.
Conclusions: Late in the clinical course, a small proportion of patients with CMT1A develop severe proximal leg weakness, and long-term follow-up is essential for its detection. MRI scans may show subclinical involvement of the thigh musculature.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None.
References
-
- Dyck P J, Lambert E H. Lower motor and primary sensory neuron diseases with peroneal muscular atrophy. I. Neurologic, genetic, and electrophysiologic findings in hereditary polyneuropathies. Arch Neurol 1968391032–1038. - PubMed
-
- Harding A E, Thomas P K. The clinical features of hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy types I and II. Brain 1980103259–280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical