Proximal tibiofibular synostosis as a source of ankle pain: a case report
- PMID: 16789462
- PMCID: PMC1888597
Proximal tibiofibular synostosis as a source of ankle pain: a case report
Erratum in
- Iowa Orthop J. 2007;27:following table of contents. Leninbabu, Vinayagam [corrected to Lenin Babu, Vinayagam]
Abstract
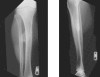
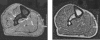
We report the case of a 61-year-old man who presented with ankle pain of unknown etiology. The actual cause for his pain was missed during his two initial visits when only ankle radiographs were taken. During his third visit, a full-length tibia film revealed a proximal tibiofibular synostosis. He successfully underwent a fibular osteotomy with complete symptomatic relief. A literature review of this topic is presented.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diaphyseal tibiofibular synostosis in a runner.J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013 Sep-Oct;52(5):638-42. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 May 31. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013. PMID: 23731941
-
Altered fibular growth patterns after tibiofibular synostosis in children.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001 Feb;83(2):247-54. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200102000-00013. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001. PMID: 11216687
-
Proximal tibiofibular synostosis.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978 Sep;(135):45-7. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978. PMID: 709951
-
Fibular stress fracture associated with distal tibiofibular synostosis in an athlete. A case report and literature review.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992 Aug;(281):195-8. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992. PMID: 1499209 Review.
-
Posttraumatic pediatric distal tibiofibular synostosis: a case report.Foot Ankle Int. 2004 Jun;25(6):429-33. doi: 10.1177/107110070402500613. Foot Ankle Int. 2004. PMID: 15215031 Review.
Cited by
-
Proximal tibiofibular synostosis as a possible cause of a pseudoradicular syndrome: a case report.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011 Dec;19(12):2115-8. doi: 10.1007/s00167-010-1379-7. Epub 2011 Jan 11. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2011. PMID: 21222100 Free PMC article.
-
A novel approach for simultaneous tibiofibular synostosis takedown and peroneus longus ligamentoplasty for posttraumatic tibiofibular synostosis: a case report and review of the literature.J Med Case Rep. 2020 Jul 5;14(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s13256-020-02397-7. J Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32622364 Free PMC article.
-
Post-traumatic synostosis of the metatarsals - a case report.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 8;25(1):894. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08024-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39516837 Free PMC article.
-
Synostosis of the proximal tibiofibular joint.Case Rep Med. 2010;2010:794594. doi: 10.1155/2010/794594. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Case Rep Med. 2010. PMID: 20592991 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral Proximal Tibiofibular Synostosis Caused by Osteochondroma in a 21-Year-Old Highly Active Male-First in Literature.Medicina (Kaunas). 2021 Oct 18;57(10):1126. doi: 10.3390/medicina57101126. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021. PMID: 34684163 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cullen JP, Pellegrini VD, Miller RJ, et al. Treatment of traumatic radio-ulnar synostosis by excision and post operative low dose irradiation. J Hand Surgery. 1994;19(3):394–401. - PubMed
-
- Gamble JG. Proximal tibiofibular synostosis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1984;4(2):243–245. - PubMed
-
- Rockwood CA, Jr, Green DP, Bucholz RW. Rockwood and Green's fractures in adults. 3rd edition. 1-2. JB Lippincott Company; 1991. pp. 717–718.pp. 2027
-
- Wong K, Weiner DS. Proximal tibiofibular synostosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1978;135:45–47. - PubMed
-
- McMaster JH, Scranton PE., Jr Tibiofibular synostosis— a cause of ankle disability. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1975;111:172–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical