A meta-analysis of the association between adherence to drug therapy and mortality
- PMID: 16790458
- PMCID: PMC1488752
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.38875.675486.55
A meta-analysis of the association between adherence to drug therapy and mortality
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the relation between adherence to drug therapy, including placebo, and mortality.
Design: Meta-analysis of observational studies.
Data sources: Electronic databases, contact with investigators, and textbooks and reviews on adherence. Review methods Predefined criteria were used to select studies reporting mortality among participants with good and poor adherence to drug therapy. Data were extracted for disease, drug therapy groups, methods for measurement of adherence rate, definition for good adherence, and mortality.
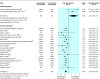
Results: Data were available from 21 studies (46,847 participants), including eight studies with placebo arms (19,633 participants). Compared with poor adherence, good adherence was associated with lower mortality (odds ratio 0.56, 95% confidence interval 0.50 to 0.63). Good adherence to placebo was associated with lower mortality (0.56, 0.43 to 0.74), as was good adherence to beneficial drug therapy (0.55, 0.49 to 0.62). Good adherence to harmful drug therapy was associated with increased mortality (2.90, 1.04 to 8.11).
Conclusion: Good adherence to drug therapy is associated with positive health outcomes. Moreover, the observed association between good adherence to placebo and mortality supports the existence of the "healthy adherer" effect, whereby adherence to drug therapy may be a surrogate marker for overall healthy behaviour.
Figures
Comment in
-
The healthy adherer and the placebo effect.BMJ. 2006 Jul 1;333(7557):18-9. doi: 10.1136/bmj.333.7557.18. BMJ. 2006. PMID: 16809709 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Review: good adherence (compared with poor adherence) to drug therapy is associated with a reduction in mortality.ACP J Club. 2006 Nov-Dec;145(3):80. ACP J Club. 2006. PMID: 17080992 No abstract available.
-
Review: good adherence to drug therapy is associated with reduced mortality.Evid Based Nurs. 2007 Jan;10(1):24. doi: 10.1136/ebn.10.1.24. Evid Based Nurs. 2007. PMID: 17218298 No abstract available.
References
-
- DiMatteo MR. Variations in patients' adherence to medical recommendations: a quantitative review of 50 years of research. Med Care 2004;42: 200-9. - PubMed
-
- Miller NH, Hill M, Kottke T, Ockene IS. The multilevel compliance challenge: recommendations for a call to action. A statement for healthcare professionals. Circulation 1997;95: 1085-90. - PubMed
-
- Morris LS, Schulz RM. Patient compliance—an overview. J Clin Pharm Ther 1992;17: 283-95. - PubMed
-
- Donovan JL. Patient decision making. The missing ingredient in compliance research. Int J Technol Assess Health Care 1995;11: 443-55. - PubMed
-
- Ellis S, Shumaker S, Sieber W, Rand C. Adherence to pharmacological interventions. Current trends and future directions. The Pharmacological Intervention Working Group. Control Clin Trials 2000;21: S218-25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical